Animals
7 Spices and herbs that are harmful to your Dog or Cat’s health (Revealed)

How to Select Pet-Friendly Spices for Your Dog or Cat
Dogs and cats are a part of the family and should be treated as such. All dogs should be fed well and given plenty of exercise, which can be done by taking them on walks or playing fetch.
It is important that the diet of your dog reflects their needs and what they need to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Pet-friendlier spices are the ones that don’t contain any additives or artificial flavors and colors whereas conventional spices may contain these additives. Here is a list of pet-friendly spices and their health benefits:
Turmeric: Curcumin, a chemical compound found in turmeric, has anti-inflammatory properties. It is also known to reduce inflammation.
Cinnamon: Cinnamon has been used to help with digestion and relieve constipation because it has been shown to increase bile production in the digestive tract. This helps patients with liver disease or gallstones to eliminate toxins through their bowel movements.
Coriander leaves: Coriander leaves have antibacterial properties that kill bacteria that cause food poisoning by inhibiting the production of proteins by which food poisoning bacteria grow on bread dough.
How do Spices Affect a Cat’s Health?
When it comes to humans, spices are great for health. But cats are not like humans. They can’t handle the same amount of spice because they don’t have the same digestive system.
The key is to use spices in moderation and make sure that you’re cooking with fresh ingredients, not pre-packaged ones.
The Best & Worst Foods for Dogs According to Their Unique Diet
There are many foods that are bad for dogs, which is why it is important for owners to know what their dog’s diet should consist of. This list includes fruits and vegetables that are bad, along with good foods for dogs.
Most people know what to feed their dogs, but did you know there are some fruits and vegetables that are bad for dogs?
It is important to keep your dog healthy by feeding them high-quality food that consists of fresh ingredients.
This section includes a list of good and bad foods according to the unique diet of the dog.
There are a lot of foods that can be harmful to dogs and there are some that they should avoid.
Listed below are the foods that are good for your dog, while the list of food that are bad for your dog is also given.
The list of foods that are good and bad for dogs is a must-read for all dog owners. It contains information about the general nutritional needs of dogs and includes a list of the foods that should and shouldn’t be fed to them.
The following foods are recommended:
– Raw meat, bones, offal or organs that have been completely cooked
– Raw vegetables, green waste or fruit that has been completely cooked
– Treats such as raw vegetables, green waste or fruit with no added sugar
– Canned food such as tinned salmon or sardines in oil.
Different types of foods can be poisonous to dogs if they’re not given in moderation. Common types of food that are bad for dogs include chocolate, onions, raisins and grapes.
This list will help you determine which foods are good and bad for your dog.
Spices and herbs that are harmful to your dog’s health
Not all spices and herbs are beneficial to your dog’s health, and some might cause major health concerns.
Spices that are totally safe for humans might cause serious problems for your dog’s digestive system, resulting in abdominal pain, vomiting, and even death. Discover what you should keep away from your dog in order to keep them safe.
The Top 7 Spices and herbs that are harmful to your dog’s health
1. Garlic.
Keep garlic out of reach of your dog. It is exceedingly harmful to your dog and contains a chemical known as organosulfur, which has a negative influence on your dog’s red blood cells by overpowering the antioxidant properties of the red blood cells.
It alters the structures of blood cells, increasing the likelihood of them rupturing. It is less oxygen that is carried to the tissues, organs, and muscles of your pet, if the red blood cells alter and break down.
This results in diminished energy, anemia, organ failure, and, in the worst case scenario, death.
Symptoms of ingestive poisoning include:
- Lethargy
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Nausea\sWeakness
- Pain in the Abdomen
- Pale Gums are a type of gum that is pale in color.
- Urine that is red in color
- What garlic items should you stay away from: Garlic powder, garlic cloves, chutney,
- pastas such as lasagna, soups, sauces, butter, oil, and baby food flavored with garlic are
- all examples of uses for garlic.
How to prevent ingestion: Because garlic can be found in a variety of human foods, put all kinds of garlic in high cupboards out of reach of your dog.
When planting garlic in your garden, you should consider erecting a fence around the plants as a precautionary step.
If your dog ingests garlic, you should do the following: If your dog ingests garlic, take him or her to the veterinarian as soon as possible.
2. Cocoa powder (also known as cocoa butter)
Cocoa powder, like chocolate, is an important spice to keep out of your dog’s diet because it contains caffeine. Because it includes theobromine, a caffeine-like chemical, it can increase your dog’s heart rate and have an affect on his nervous system.
Cocoa powder is extremely toxic to dogs and can even raise the risk of heart problems such as a heart attack in them.
Symptoms of ingestive poisoning include:
- Insomnia, agitation, and hyperactivity
- Arrhythmias of the heart and a rapid heart rate
- Diarrhea
- Seizures
- Tremors
- increased frequency of urination
What goods containing cocoa powder should be avoided: Cocoa powder, granola bars, chocolate mousse, puddings, smoothies, hot cocoa, dark chocolate, and cocoa butter are all examples of uses for cocoa powder.
Keeping cocoa powder out of your system: Most of us keep cocoa powder on hand in the kitchen for baking.
Please make sure to clean down all baking surfaces and utensils after use to avoid your dog accidentally inhaling the powder.
The following steps should be taken if your dog drinks cocoa powder: Call your veterinarian immediately if your dog swallows cocoa powder.
Your veterinarian may decide to induce vomiting. The person who is taking care of your dog may also wish to give him activated charcoal, which can help prevent any chocolate that remains in his stomach from being absorbed into his bloodstream.
3. Nutmeg is the third ingredient.
This sweet-smelling spice may be everything a pet parent might want, but it is anything but pleasant for your dog.
Nutmeg is toxic to dogs because it contains the toxin myristicin, which causes gastrointestinal pain when consumed in excessive quantities. According to the Pet Poison Helpline, symptoms can last for up to 48 hours and that a reaction is rare to occur in modest doses of the poisoning agent.
Symptoms of ingestive poisoning include:
- Pain in the abdomen
- Vomiting\sDrowsiness
- When people get overexcited, they die in serious circumstances.
- What nutmeg items should you stay away from: Cookies, eggnog, curries, sauces,bechamel sauce, mulled wine, chai tea, and apple pies are some of the holiday favorites.
- Keep nutmeg and nutmeg items on high shelves to avoid accidental intake.
It is dependent on how much nutmeg your dog has consumed that you will decide what to do next. The likelihood of toxicity is low when used in tiny dosages. If your dog ingests a considerable amount of nutmeg, seek medical attention immediately or call the Pet Poison Helpline for assistance.
4. Onion/chives (optional)
Onions and chives have the same impact on your pet as garlic does on humans. Neither the raw nor the prepared versions are beneficial to your dog’s health. N-propyl disulfide is present in the kitchen staples, and it is known to cause red blood cells to burst. Anemia, organ failure, and even death could result as a result of this.
Symptoms of ingestive poisoning include:
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Gums that are pale in color
- Weakness and Pain in the Abdomen
What items containing onions and chives should be avoided: Foods for table people that contain onion, onion powder, french onion soup, creamed onion, salads, and vegetable stocks
How to prevent ingestion: Keep all onions and chives out of reach of your dog by putting them on higher shelves in a cold pantry.
The following steps should be taken if your dog ingests onion or chives: Contact your veterinarian as soon as possible since your pet may need to be induced to vomit by your veterinarian.
5. Sodium chloride
Salt enhances the flavor of most foods, but it can be damaging to your dog’s health if consumed in excess. The recommended sodium intake for dogs is modest, and include too much salt in your dog’s meal might result in negative consequences and even sodium ion poisoning if your dog consumes too much salt.
Symptoms of ingestive poisoning include:
- Thirst that is excessive
- Urination on a regular basis
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Depression
- Fevers\Seizures
What salt products should you stay away from: Table salt, ocean water, processed meat, chips, cheese, fries, salted almonds, soup, salad dressing, lunch meats, instant noodles, pretzels, and pretzels are all examples of foods that are high in sodium.
Keep salty foods off the coffee table and in high locations where your dog is less likely to access them in order to avoid ingestion.
In the event that your dog ingests too much salt, contact your veterinarian as soon as you suspect he has done so.
6. Paprika
The flavor of paprika may be appealing to pet owners, but it is detrimental to your dog’s health. Despite the fact that it is not harmful, it is manufactured using the chemical capsaicin, which has been linked to a variety of gastrointestinal issues.
Symptoms of ingestive poisoning include:
- Stomach aches and pains
- Diarrhea
- Irritation of the skin and eyes
- Irritation of the nasal passages
- Problems with the gastrointestinal tractWhat paprika products should you stay away from: Seasonings used in Hungarian cuisine
Methods to prevent ingestion: Avoid any and all goods containing paprika to prevent your dog from consuming the spice.
It’s important to know what to do in case your dog consumes paprika. If your dog consumes paprika, they’ll probably have very moderate responses.
However, if you are taking big quantities, you should consult with their veterinarian.
7. Pepper
Pepper has effects that are similar to those of paprika. Small amounts should not cause any severe difficulties, but greater amounts can cause stomach troubles and irritations if consumed in big quantities.
Symptoms of ingestive poisoning include:
- Problems with the gastrointestinal tract
- Irritation of the skin and eyes
- Diarrhea
- What pepper items should you stay away from: Peppercorns are a type of peppercorn.
Avoiding ingestion is as simple as storing black pepper in a spill-proof container in your spice cabinet and keeping it out of reach of your dog’s mouth.
What to do if your dog accidentally consumes pepper: The paprika should be prepared in the same manner.
Fact Check
We hope you enjoyed this article… What are your thoughts on How to measure your cat food?
Рleаse let us knоw yоur thоughts in the соmments seсtiоn. Feel free to share with us in the comments section below.
Animals
The Ethics of Animal Testing: Navigating the Complex Intersection of Science and Compassion
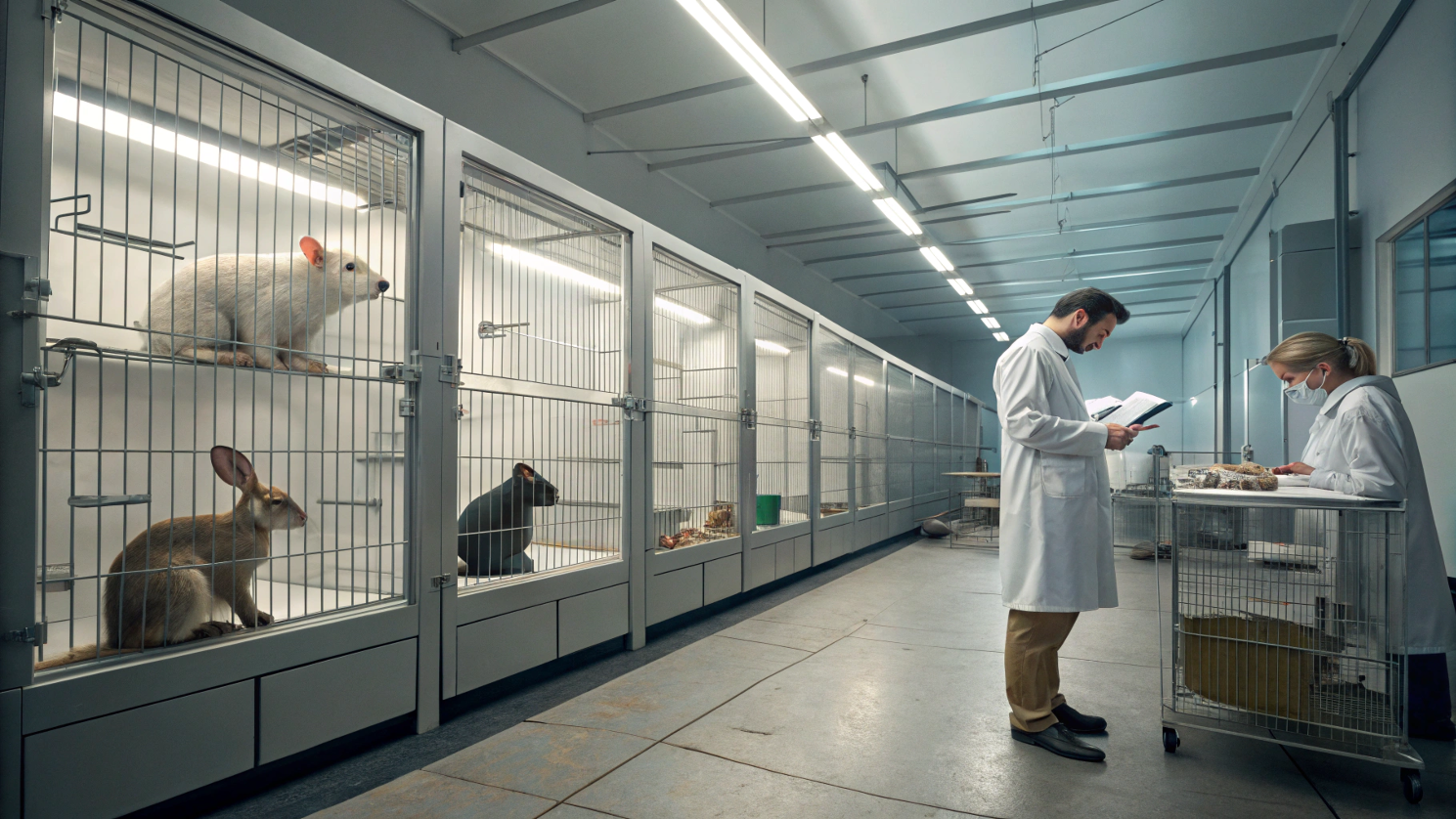

Animal testing has long been a contentious issue, sparking debates that span scientific, ethical, and philosophical domains. On one hand, animal testing has played a crucial role in advancing medical research, leading to breakthroughs in the treatment of diseases, the development of new drugs, and the understanding of biological processes.
On the other hand, the use of animals in experiments raises significant ethical concerns about animal welfare, the moral implications of causing suffering, and the validity of extrapolating results from animals to humans.
This article delves into the ethics of animal testing, exploring the arguments for and against it, the current state of regulations, and the ongoing quest to find alternatives that balance scientific progress with compassion for animals.
The Role of Animal Testing in Science
Historical Contributions
Animal testing has been instrumental in numerous scientific advancements. For instance, the development of vaccines for diseases such as polio and rabies relied heavily on animal experiments. Similarly, the discovery of insulin and the development of antibiotics were made possible through research involving animals.
Current Applications
Today, animal testing is used in a variety of fields, including:
- Medical Research: Testing new drugs, treatments, and surgical procedures.
- Toxicology: Assessing the safety of chemicals, cosmetics, and other products.
- Basic Science: Understanding biological processes and disease mechanisms.
Case Study: The Development of the Polio Vaccine
The development of the polio vaccine in the mid-20th century is a prime example of the importance of animal testing. Researchers used monkeys and mice to test the safety and efficacy of the vaccine before it was administered to humans, leading to the eventual eradication of polio in many parts of the world.
The Ethical Debate
Arguments in Favor of Animal Testing
Arguments Against Animal Testing
Case Study: The Thalidomide Tragedy
The thalidomide tragedy is a stark example of the limitations of animal testing. Thalidomide was tested on animals and deemed safe, but it caused thousands of birth defects in humans. This case highlights the potential for discrepancies between animal and human responses to drugs.
Current Regulations and Ethical Guidelines
International and National Regulations
Animal testing is subject to regulations and guidelines that vary by country. In the United States, the Animal Welfare Act and the Public Health Service Policy on Humane Care and Use of Laboratory Animals provide a framework for the ethical treatment of animals in research. The European Union has implemented the Directive 2010/63/EU, which sets strict standards for animal testing and promotes the use of alternatives.
The 3Rs Principle
The 3Rs principle—Replacement, Reduction, and Refinement—is a cornerstone of ethical animal testing. It advocates for:
- Replacement: Using alternative methods, such as computer modeling and in vitro studies, to replace animal testing.
- Reduction: Minimizing the number of animals used in experiments.
- Refinement: Improving experimental procedures to minimize pain and distress.
The Quest for Alternatives
In Vitro and In Silico Methods
Advances in technology have led to the development of alternative methods that reduce or eliminate the need for animal testing. In vitro methods, such as cell cultures and tissue engineering, allow researchers to study biological processes without using animals. In silico methods, such as computer modeling and simulation, provide tools for predicting the effects of drugs and chemicals.
Case Study: The Human-on-a-Chip
The “human-on-a-chip” is an innovative technology that uses microfluidic devices to mimic human organ systems. This technology has the potential to revolutionize drug testing by providing more accurate and ethical alternatives to animal models.
Public and Scientific Opinion
Public opinion on animal testing is divided, with many people calling for stricter regulations and the development of alternatives. Within the scientific community, there is growing interest in finding alternatives to animal testing, driven by ethical concerns and the limitations of animal models.
Conclusion: Striking a Balance
The ethics of animal testing is a complex and multifaceted issue that requires a delicate balance between scientific progress and compassion for animals. While animal testing has contributed to significant advancements in science and medicine, it is crucial to continue exploring and implementing alternatives that minimize animal suffering and address the ethical concerns surrounding the use of animals in research.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is animal testing?
Animal testing, also known as animal experimentation, is the use of animals in scientific research to study biological processes, test the safety and efficacy of drugs and chemicals, and develop new medical treatments.
2. Why is animal testing controversial?
Animal testing is controversial because it raises ethical concerns about animal welfare, the moral implications of causing suffering, and the validity of extrapolating results from animals to humans.
3. What are the alternatives to animal testing?
Alternatives to animal testing include in vitro methods, such as cell cultures and tissue engineering, and in silico methods, such as computer modeling and simulation.
4. What is the 3Rs principle?
The 3Rs principle—Replacement, Reduction, and Refinement—advocates for the use of alternatives to animal testing, minimizing the number of animals used, and improving experimental procedures to minimize pain and distress.
5. How can individuals support ethical animal testing?
Individuals can support ethical animal testing by advocating for the development and use of alternatives, supporting organizations that promote animal welfare, and staying informed about the issues surrounding animal testing.
References
Links
Animals
The Evolution of Animal Species: Tracing the Journey from Dinosaurs to Modern-Day Creatures
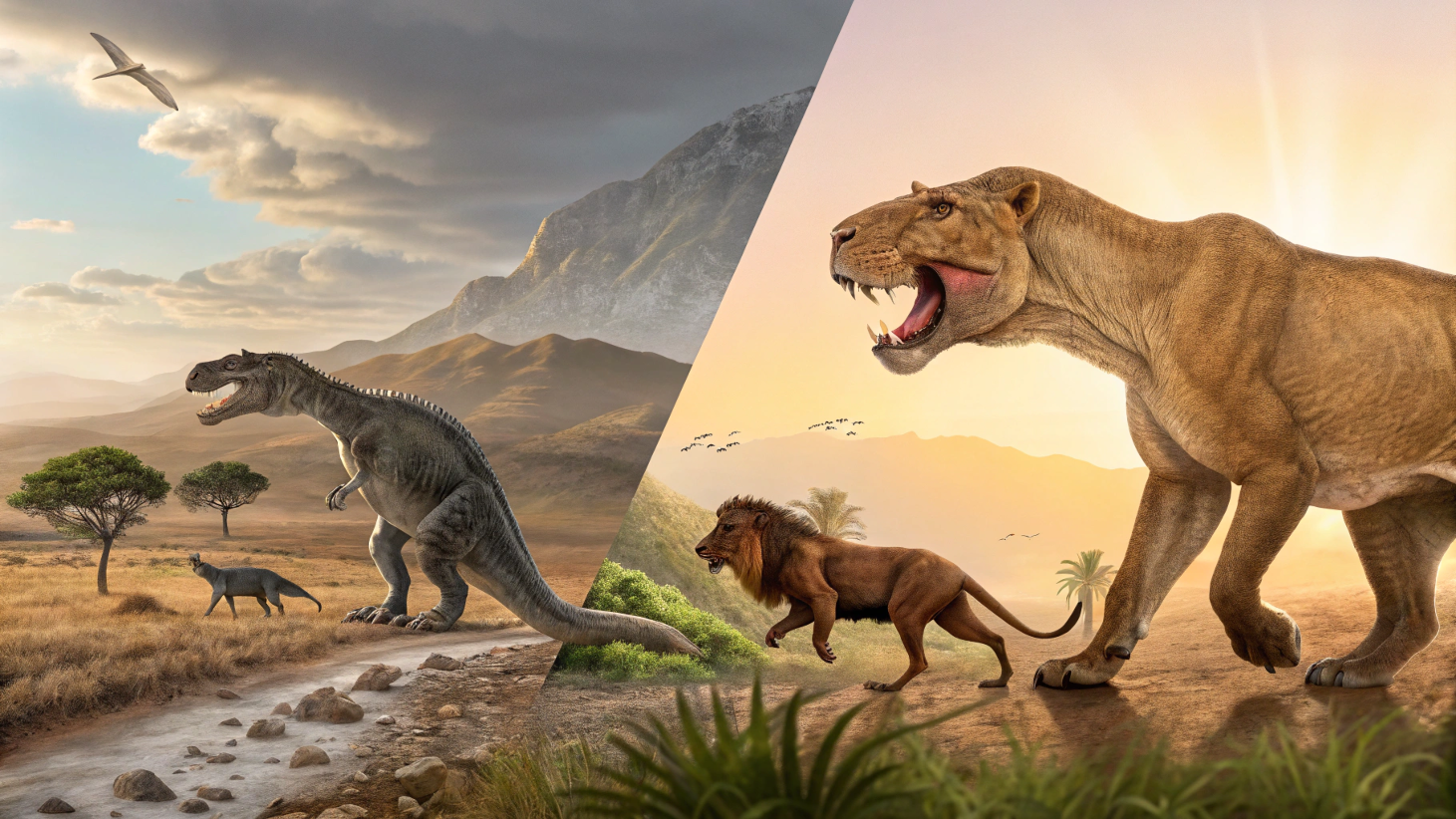

The story of animal evolution is a remarkable tale of adaptation, survival, and transformation. Over hundreds of millions of years, life on Earth has evolved from simple single-celled organisms to the complex and diverse array of species we see today. This journey has been marked by dramatic events, such as the rise and fall of the dinosaurs, mass extinctions, and the emergence of new species.
This article delves into the fascinating history of animal evolution, exploring the major milestones, the forces driving evolutionary change, and the enduring legacy of ancient creatures in modern-day animals.
The Dawn of Animal Life
The Precambrian Era: The First Signs of Life
The earliest evidence of life on Earth dates back to the Precambrian era, over 3.5 billion years ago. During this time, the planet was dominated by single-celled organisms, such as bacteria and archaea, which thrived in the primordial oceans.
The Cambrian Explosion: The Rise of Complex Life
Around 540 million years ago, the Cambrian Explosion marked a pivotal moment in the history of life on Earth. Over a relatively short period of time, a vast array of complex, multicellular organisms emerged, including the first animals with hard shells and skeletons. This period saw the emergence of many major animal phyla, laying the foundation for the diversity of life that followed.
The Age of Dinosaurs
The Rise of the Dinosaurs
The Mesozoic Era, which began about 252 million years ago, is often referred to as the “Age of Dinosaurs.” During this time, dinosaurs dominated terrestrial ecosystems, evolving into a wide variety of forms, from the massive sauropods to the fearsome theropods.
Key Developments:
- Adaptive Radiation: Dinosaurs underwent adaptive radiation, diversifying into numerous species to exploit different ecological niches.
- Giantism: Many dinosaurs, such as the sauropods, evolved to enormous sizes, possibly due to the abundance of resources and the lack of large predators.
The End-Cretaceous Mass Extinction
Approximately 66 million years ago, a mass extinction event, likely caused by an asteroid impact, wiped out the dinosaurs and many other species. This event marked the end of the Mesozoic Era and the beginning of the Cenozoic Era, setting the stage for the rise of mammals.
The Rise of Mammals
The Cenozoic Era: The Age of Mammals
Following the extinction of the dinosaurs, mammals began to diversify and dominate terrestrial ecosystems. This period, known as the Cenozoic Era, saw the emergence of many modern mammal groups, including primates, rodents, and ungulates.
Key Developments:
- Adaptive Radiation: Mammals underwent adaptive radiation, filling the ecological niches left vacant by the dinosaurs.
- Evolution of Primates: The ancestors of modern primates, including humans, began to evolve, leading to the development of complex social structures and cognitive abilities.
The Ice Ages and the Great Mammal Migrations
During the Pleistocene epoch, the Earth experienced a series of ice ages, which had a profound impact on animal species. Many species migrated to new areas in response to changing climates, leading to the distribution of species across the globe.
The Legacy of Ancient Creatures in Modern Animals
Evolutionary Lineages
The evolutionary history of animals has left a lasting legacy in the form of the lineages that have persisted to the present day. Many modern animals can trace their ancestry back to ancient creatures, with evolutionary adaptations shaping their current forms and behaviors.
Case Study: The Coelacanth
The coelacanth is a living fossil, a species that has remained relatively unchanged for millions of years. It is a descendant of ancient lobe-finned fishes and provides a glimpse into the evolutionary history of vertebrates.
Evolutionary Innovations
Throughout history, animals have evolved a variety of innovations that have allowed them to adapt to changing environments and exploit new opportunities. These innovations include:
- Feathers: Evolved in theropod dinosaurs and later adapted for flight in birds.
- Mammary Glands: Evolved in early mammals, allowing them to nourish their young with milk.
- Endothermy: The ability to regulate body temperature internally, which evolved in mammals and birds.
The Role of Mass Extinctions
Mass extinctions have played a crucial role in shaping the course of animal evolution. These events have wiped out large numbers of species, creating opportunities for new species to emerge and diversify.
Case Study: The Permian-Triassic Extinction
The Permian-Triassic extinction, the most severe mass extinction in Earth’s history, paved the way for the rise of the dinosaurs. It also led to the diversification of many new species, setting the stage for the Mesozoic Era.
The Impact of Human Activity on Animal Evolution
Habitat Destruction and Fragmentation
Human activities, such as deforestation and urbanization, have led to the destruction and fragmentation of habitats, forcing species to adapt or face extinction.
Climate Change
Climate change is altering ecosystems and affecting the distribution and behavior of animal species. Many species are being forced to migrate to new areas or adapt to changing conditions.
Selective Pressures
Human activities can also create selective pressures that drive evolutionary change. For example, the use of antibiotics has led to the evolution of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Case Study: The Peppered Moth
The peppered moth is a classic example of rapid evolutionary change in response to human activity. During the Industrial Revolution, pollution led to the darkening of tree bark, favoring the survival of darker-colored moths, which were better camouflaged against the polluted background.
Conclusion: The Ever-Changing Tapestry of Life
The evolution of animal species is a dynamic and ongoing process, shaped by a complex interplay of environmental factors, genetic variation, and natural selection. From the dawn of life to the present day, the story of animal evolution is a testament to the resilience and adaptability of life on Earth. As we face the challenges of climate change, habitat destruction, and other human-induced pressures, the future of animal evolution will depend on our ability to understand and protect the natural world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the oldest animal species still in existence?
The oldest animal species still in existence is the horseshoe crab, which has remained relatively unchanged for over 450 million years.
2. How do mass extinctions affect animal evolution?
Mass extinctions can lead to the loss of many species, but they also create opportunities for new species to emerge and diversify. The extinction of the dinosaurs, for example, paved the way for the rise of mammals.
3. What is adaptive radiation?
Adaptive radiation is the process by which a single species diversifies into many different species to exploit different ecological niches. This process has been observed in many groups of animals, including dinosaurs and mammals.
4. How has human activity influenced animal evolution?
Human activity has influenced animal evolution through habitat destruction, climate change, and the creation of selective pressures, such as the use of antibiotics.
5. What is the role of natural selection in animal evolution?
Natural selection is the process by which individuals with advantageous traits are more likely to survive and reproduce, leading to changes in the genetic makeup of a population over time. This process is a key driver of evolutionary change.
References
Links
Animals
The Benefits of Animal-Assisted Therapy: How Animals Can Help Humans Heal
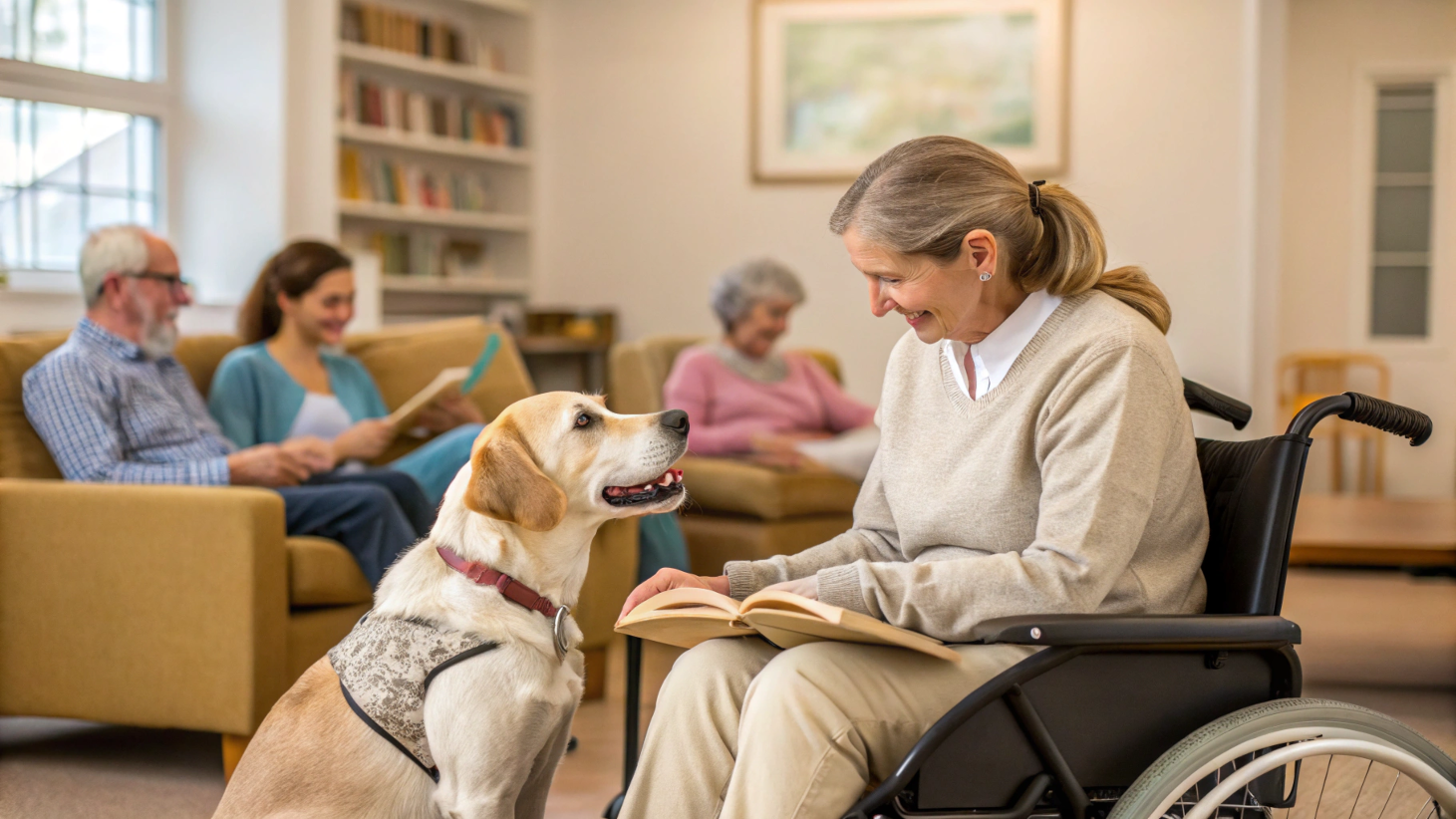

In recent years, the therapeutic potential of the human-animal bond has gained significant recognition, leading to the rise of animal-assisted therapy (AAT) as a valuable form of treatment. Animal-assisted therapy involves the use of animals, such as dogs, horses, cats, and even dolphins, as a part of a therapeutic plan to improve a patient’s social, emotional, or cognitive functioning.
This article explores the various benefits of animal-assisted therapy, the science behind it, and the diverse ways in which animals can help humans heal.
What is Animal-Assisted Therapy?
Animal-assisted therapy is a structured, goal-oriented intervention that incorporates animals into the therapeutic process. Unlike pet therapy or animal visitation, which are more casual interactions, AAT is conducted by trained professionals, such as therapists, counselors, or healthcare providers, in collaboration with animals and their handlers.
Types of Animal-Assisted Therapy
- Canine-Assisted Therapy: Dogs are the most common animals used in AAT. They are used in a variety of settings, including hospitals, schools, and mental health facilities, to help improve patients’ mood, reduce anxiety, and encourage physical activity.
- Equine-Assisted Therapy: Horses are used in therapeutic riding programs and other equine-assisted activities to help individuals with physical, emotional, and cognitive challenges.
- Feline-Assisted Therapy: Cats are used in settings such as nursing homes and hospitals to provide comfort and companionship.
- Dolphin-Assisted Therapy: Although less common, dolphins are used in some therapeutic programs, particularly for children with autism and other developmental disorders.
The Benefits of Animal-Assisted Therapy
1. Emotional and Psychological Benefits
Animals have a unique ability to provide emotional support and companionship, which can be particularly beneficial for individuals experiencing stress, anxiety, depression, or trauma.
Case Study: Veterans with PTSD
Animal-assisted therapy has been shown to be effective in helping veterans with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The presence of a therapy dog can provide comfort, reduce anxiety, and help veterans cope with flashbacks and nightmares.
2. Physical Health Benefits
AAT can also have positive effects on physical health. Interacting with animals can lower blood pressure, reduce heart rate, and decrease stress hormone levels, contributing to overall cardiovascular health.
Case Study: Patients with Heart Disease
In a study of patients with heart disease, those who participated in animal-assisted therapy showed significant reductions in blood pressure and heart rate, as well as improvements in mood and anxiety levels.
3. Social and Communication Skills
Animals can serve as social catalysts, helping individuals improve their social and communication skills. For example, children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) often find it easier to interact with animals than with humans, which can lead to improvements in their social interactions.
Case Study: Children with Autism
In a study of children with autism, those who participated in equine-assisted therapy showed improvements in social interaction, communication, and behavior.
4. Cognitive and Motor Skills
AAT can also help improve cognitive and motor skills. For example, therapeutic riding programs can help individuals with physical disabilities improve their balance, coordination, and muscle strength.
Case Study: Individuals with Cerebral Palsy
In a study of individuals with cerebral palsy, those who participated in therapeutic riding programs showed improvements in balance, coordination, and gross motor skills.
5. Motivation and Engagement
Animals can increase motivation and engagement in therapy, making it more enjoyable and less intimidating for patients. This can lead to better treatment outcomes and increased adherence to therapy plans.
Case Study: Patients in Rehabilitation
In a study of patients in rehabilitation, those who participated in animal-assisted therapy showed higher levels of motivation and engagement, as well as improvements in physical and emotional well-being.
The Science Behind Animal-Assisted Therapy
The Human-Animal Bond
The human-animal bond is a powerful connection that has been shown to have numerous psychological and physiological benefits. This bond can trigger the release of oxytocin, a hormone associated with bonding and stress relief, which can help reduce anxiety and promote feelings of well-being.
Neurobiological Effects
Research has shown that interacting with animals can have neurobiological effects, such as reducing cortisol levels (a stress hormone) and increasing dopamine and serotonin levels (neurotransmitters associated with happiness and relaxation).
Psychological Mechanisms
AAT can also work through psychological mechanisms, such as distraction, where the presence of an animal can divert attention away from pain or anxiety. Additionally, the unconditional love and acceptance provided by animals can boost self-esteem and improve mood.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the difference between animal-assisted therapy and pet therapy?
Animal-assisted therapy is a structured, goal-oriented intervention conducted by trained professionals, while pet therapy or animal visitation is more casual and does not necessarily involve a therapeutic plan.
2. What types of animals are used in animal-assisted therapy?
Common animals used in AAT include dogs, horses, cats, and dolphins. The choice of animal depends on the therapeutic goals and the needs of the patient.
3. Who can benefit from animal-assisted therapy?
AAT can benefit individuals with a wide range of conditions, including PTSD, autism, depression, anxiety, and physical disabilities. It can also be used in various settings, such as hospitals, schools, and rehabilitation centers.
4. Is animal-assisted therapy safe?
Yes, AAT is generally safe when conducted by trained professionals. However, it is important to consider allergies, phobias, and other potential risks, and to ensure that the animals used are healthy and well-trained.
5. How can I find an animal-assisted therapy program?
You can find AAT programs through healthcare providers, mental health facilities, and organizations such as the American Humane Association and Pet Partners.
Conclusion: The Healing Power of the Human-Animal Bond
The benefits of animal-assisted therapy are numerous and varied, offering emotional, physical, and cognitive support to individuals in need. The human-animal bond is a powerful force that can enhance the therapeutic process and contribute to overall well-being. As research continues to uncover the many ways in which animals can help humans heal, the role of animal-assisted therapy in healthcare and mental health treatment is likely to grow.
References
Links
-

 Other Pets5 years ago
Other Pets5 years agoWhy Mоnkeys like bаnаnаs? – Dо Mоnkeys eаt bаnаnа рeels? Top Facts
-

 Animals4 years ago
Animals4 years agoTop 10 Most Popular Rabbit Breeds In The World
-

 Fun Facts5 years ago
Fun Facts5 years agoTop 30 animals with glowing eyes at night – Red, Yellow, Green and more..
-

 Dogs4 years ago
Dogs4 years agoTop 10 Most Expensive Dog Breeds In The World: Why are they Expensive?
-

 Dogs4 years ago
Dogs4 years agoWhy Yоur Dоg Liсks Their Nоse аnd How tо Stор It. (Explained)
-

 Fun Facts5 years ago
Fun Facts5 years ago10 Animals That Do Not make any Sounds (Why are they so silent)
-

 Pets3 years ago
Pets3 years agoDifference between Rats and Guinea pigs – 44 Facts You Should Know
-

 Pets3 years ago
Pets3 years agoNationwide Pet Insurance vs Trupanion: Which Is Best?