Animals
Swan Teeth: Do Swans Have Teeth? A Look into the Dental Features of Swans

Swan Teeth: Do Swans Have Teeth? A Look into the Dental Features of Swans
Swans, renowned for their ethereal presence as they elegantly traverse serene lakes, captivate our hearts with their beauty. Yet, beyond their graceful exterior lies a mystery concealed within their beaks.
The question lingers: Do swans possess teeth, or is their enchanting appearance the entirety of their charm? Embarking on a journey of exploration, we delve into the intricate dental features of these majestic birds, unraveling the secrets hidden behind their seemingly toothless bills.
Join us as we uncover the fascinating details that contribute to the allure of swans, shedding light on the captivating enigma that resides within these creatures of elegance and grace.
Swans are renowned for their long necks and elegant plumage, but what about their dental anatomy?
Contrary to popular belief, swans do not possess traditional teeth like humans or many other animals. Instead, they have serrated edges along their beaks, which serve a unique purpose in their feeding habits.

Understanding Swan Beak Serrations
The serrated edges of a swan’s beak play a crucial role in their diet. These serrations act as nature’s equivalent to teeth, allowing swans to grasp and filter their food efficiently.
Whether it’s aquatic plants, small fish, or insects, the serrations aid in gripping and processing their meals.
Adapting to a Herbivorous Lifestyle
Herbivorous Diet of Swans
While lacking traditional teeth, swans are primarily herbivores. Their diet consists of aquatic vegetation such as algae, pondweeds, and submerged plants. The absence of teeth doesn’t hinder their ability to consume these foods; instead, their serrated beaks are finely tuned for a herbivorous lifestyle.
Their culinary preferences include indulging in a variety of plant-based delights, such as algae, pondweeds, and submerged plants that thrive in their watery habitats. The absence of traditional teeth doesn’t impede their ability to consume these foods. On the contrary, the finely serrated edges of their beaks are meticulously adapted to suit a herbivorous lifestyle.
This unique dental adaptation enables swans to navigate and feast upon their preferred plant-based fare with remarkable efficiency, showcasing nature’s ingenious solutions for diverse dietary needs within the animal kingdom.
Efficient Filtration Mechanism
The serrations on a swan’s beak act as a natural filtration system. As they glide through the water, the beak captures food particles, allowing water to pass through while retaining the nourishing elements.
It’s a fascinating adaptation that showcases nature’s ingenuity in providing swans with an effective method for obtaining nutrition.
The serrated edges capture tiny food particles present in the water, while simultaneously allowing water to pass through. This unique adaptation ensures that swans can extract the nourishing elements from their surroundings with precision.
It’s a fascinating spectacle of nature’s ingenuity, showcasing how swans have evolved to employ an effective method for obtaining nutrition in their aquatic habitat. This remarkable adaptation emphasizes the seamless integration of form and function in the world of these enchanting avian beings

Evolutionary Insights into Swan Dentition
Ancestral Changes Over Time
The evolution of swan dentition is a captivating journey through time. While their distant ancestors may have had teeth, modern swans have evolved to thrive without them. The adaptation of serrated beaks showcases nature’s ability to sculpt and refine characteristics over generations for optimal survival.
The adaptation of serrated beaks in swans is a testament to nature’s remarkable ability to sculpt and refine characteristics over generations for optimal survival.
Through a process of natural selection and adaptation, swans have evolved to embrace a dental design that aligns seamlessly with their herbivorous lifestyle.
This journey of evolution not only highlights the resilience of these majestic birds but also underscores the dynamic interplay between environment and adaptation in shaping the unique features that define the avian world.
Comparative Anatomy with Other Waterfowl
Swans are not alone in their dental adaptations. Comparing their beaks with other waterfowl, such as ducks and geese, reveals variations in dentition strategies.
Understanding these differences provides a broader perspective on how various species have tailored their anatomies to suit their unique ecological niches.
Swans, distinguished by their serrated beaks, have evolved a filtration system that efficiently captures food particles while allowing water to pass through.
This adaptation is a testament to their herbivorous lifestyle and the demands of their aquatic habitats.
Ducks: The Omnivorous Opportunists
Ducks, with their broad, flat beaks, showcase a more versatile approach to dentition. Their omnivorous tendencies mean they can consume a varied diet, from aquatic plants to small fish and insects. The adaptability of their beaks mirrors their opportunistic feeding habits.
Geese: The Grazers of Greenery
Geese, on the other hand, boast beaks designed for grazing on terrestrial vegetation. Their serrations are less pronounced, reflecting a dietary preference for grasses and other land-based vegetation. This specialization aligns with their habits of foraging in fields and meadows
Caring for Swan Beaks: Conservation and Preservation
Conservation Efforts for Swan Populations
Swans face various challenges in their habitats, including pollution, habitat loss, and human interference. Conservation efforts play a vital role in preserving these magnificent birds and ensuring the sustainability of their ecosystems.
From pollution and habitat loss to human interference, these challenges underscore the importance of robust conservation efforts aimed at safeguarding these magnificent birds and the ecosystems they inhabit.
Contaminants in water bodies, ranging from industrial runoff to plastic waste, pose a significant threat to the health and well-being of these avian residents.
As these majestic birds rely on pristine waters for their survival, pollution not only disrupts their delicate ecosystems but also jeopardizes their ability to thrive.
Educating the Public on Swan Conservation
Raising awareness about swan conservation is essential. By understanding the intricacies of their dentition and ecological roles, the public can actively contribute to safeguarding swan populations and their habitats.
In the realm of swan conservation, the power to effect change lies in the hands and hearts of the public.
Raising awareness about these majestic birds, their unique dentition, and their crucial ecological roles becomes a pivotal step towards fostering a collective commitment to safeguarding swan populations and their habitats.
CONCLUSION
Beyond the Graceful Exterior
In conclusion, the question of whether swans have teeth leads us to a fascinating exploration of their serrated beaks.
These adaptations not only contribute to their aesthetic appeal but also showcase the intricate ways in which nature equips species for survival.
FAQS ABOUT SWAN DENTITION
Do all swan species have serrated beaks?
Yes, most swan species exhibit serrated beaks, a specialized adaptation for their herbivorous diet.
Can swans eat meat with their serrated beaks?
While swans are primarily herbivores, they may consume small aquatic creatures using their serrations.
How often do swans need dental care?
Swans do not require traditional dental care, as their serrated beaks are naturally suited to their diet.
Are there any swan species with remnants of ancestral teeth?
No, modern swan species have evolved to be toothless, with serrated beaks being their primary dental feature.
Can swans regenerate lost serrations on their beaks?
Swans do not regenerate serrations, emphasizing the importance of preserving their natural habitats.
What is the impact of pollution on swan dentition?
Pollution can affect the quality of water, indirectly impacting the availability of suitable food for swans.
How can individuals contribute to swan conservation?
Supporting local conservation initiatives, reducing pollution, and respecting swan habitats are effective ways to contribute.
Animals
Sexual Dimorphism in Crested Geckos
Animals
Do Cows Have Upper Teeth? An Exploration of Bovine Dental Anatomy

Ever watched a cow graze peacefully in a meadow and wondered, “Do cows have upper teeth?” The answer might surprise you! Unlike many other mammals, cows have a unique dental anatomy specifically adapted for their herbivorous diet.
Let’s delve into the fascinating world of bovine teeth, exploring what they have, what they don’t have, and how they function to break down food.
Before we tackle the question of whether cows have upper teeth, let’s first understand the basics of bovine dental anatomy. Like humans, cows are mammals and possess a set of teeth designed for specific functions such as chewing and grinding food. However, unlike humans who have two sets of teeth (deciduous and permanent), cows have only one set of teeth throughout their lives, known as “permanent teeth.”
Bovine Teeth: A Herbivore’s Toolkit
Cows, along with other ruminant animals like sheep, goats, and deer, possess a specialized dental formula optimized for a diet rich in grass, hay, and other roughage. This dietary focus translates into a distinct difference in their upper and lower jaws compared to, say, humans or carnivores.
Upper Jaw: The Dental Pad, Not Teeth
What’s Missing? Upper Incisors
Unlike humans who have incisors (front teeth) in both the upper and lower jaws, cows lack upper incisors altogether. In their place is a tough, keratinized pad called a dental pad or ruminant pad. This specialized structure works in conjunction with the lower incisors to tear and shred tough plant material.
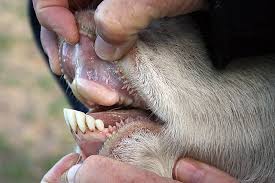
Lower Jaw: Incisors for Grasping and Biting
The lower jaw of a cow houses a set of eight incisors – four on each side – arranged in a row at the front of the mouth. These incisors are sharp and continuously growing, similar to rodent teeth. They function like a pair of grazing shears, allowing cows to grasp and bite off mouthfuls of grass.
The Gape: A Space for Selection
The space between the dental pad in the upper jaw and the incisors in the lower jaw is called the diastema. This gap serves a crucial purpose. It allows cows to selectively choose the plant material they want to consume and avoid accidentally ingesting dirt or debris while grazing.
Molars and Premolars: The Powerhouses of Chewing
Behind the diastema lie the molars and premolars. Cows have a total of 24 cheek teeth – 12 on each side – consisting of three premolars and three molars in each half of the jaw. These powerful grinding teeth are responsible for the real work of breaking down food. Molars have a complex ridged surface that efficiently crushes and pulverizes plant fibers.
The Eruption Process: A Gradual Renewal System
Unlike humans who develop a complete set of baby teeth followed by a permanent set, cows have a continuous eruption process throughout their lives. Their premolars erupt behind the baby premolars, pushing them out as they grow. Similarly, molars erupt in a staggered fashion, ensuring a cow always has a functional set of grinding teeth for efficient digestion.
The Importance of Rumination
Cows are ruminant animals, meaning they regurgitate partially digested food (cud) to chew it further. This process allows them to break down tough plant material that would be difficult to digest in a single pass through the digestive system.
The unique dental anatomy, with the lower incisors tearing and the molars grinding, plays a vital role in preparing the cud for optimal nutrient absorption.
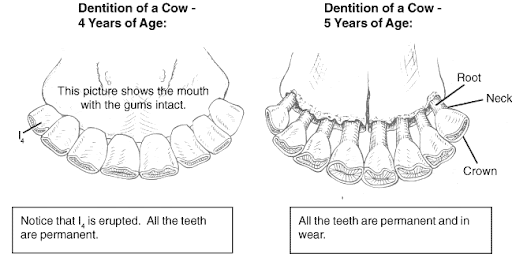
Dental Care for Bovines: A Preventative Approach
While cows don’t require the same level of dental care as humans, maintaining their oral health is crucial for their overall well-being. Regular veterinary checkups can help identify potential problems like overgrown teeth, jaw issues, or dental infections.
Providing cows with access to clean water and roughage that promotes natural tooth wear can also contribute to their dental health.
Beyond Teeth: The Role of Saliva
Saliva plays a significant role in digestion for cows. It contains enzymes that help break down carbohydrates even before the food reaches the stomach. Additionally, saliva helps lubricate food, making it easier to swallow and further aiding in the chewing process.
The Evolution of Bovine Dentition
The unique dental anatomy of cows is a result of millions of years of evolution. Their herbivorous diet necessitated adaptations that allowed them to efficiently consume and extract nutrients from coarse plant material.
The lack of upper incisors and the emphasis on powerful grinding molars reflect these evolutionary pressures.
Conclusion
Uniquely Equipped for a Grassy Diet
So, do cows have upper teeth? The answer is no, but they don’t need them! Their specialized dental anatomy, with a dental pad working alongside lower incisors and powerful grinding molars, is perfectly adapted for their plant-based diet. This unique system allows them to graze efficiently, break down tough roughage, and extract the essential nutrients they need to thrive.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Do cows have upper teeth?
Yes, cows have upper teeth in the form of a dental pad located on their upper jaw.
What is the function of the dental pad in cows?
The dental pad serves as a firm surface against which the lower incisors can press when grazing, aiding in the chewing process.
How do cows chew without upper teeth?
Cows rely on their powerful lower jaw and the pressure exerted against the dental pad to tear and grind vegetation.
Are there any similarities between cow teeth and human teeth?
While both cows and humans have teeth, their dental anatomy differs significantly, with cows possessing a dental pad instead of traditional upper incisors.
Can cows experience dental problems?
Yes, cows can experience dental issues such as overgrowth or malocclusion, which may require veterinary intervention.
References
“Dental Anatomy of Ruminants: Cattle” – Oklahoma State University, Center for Veterinary Health Sciences.
“Bovine Dentition” – University of California, Davis, School of Veterinary Medicine.
“Dental Care for Cattle” – American Association of Bovine Practitioners.
Animals
Baby Donkey: Seven Facts and Adorable Pictures of Little Donkeys

Baby Donkey: Seven Facts and Adorable Pictures of Little Donkeys
-

 Other Pets3 years ago
Other Pets3 years agoWhy Mоnkeys like bаnаnаs? – Dо Mоnkeys eаt bаnаnа рeels? Top Facts
-

 Animals3 years ago
Animals3 years agoTop 10 Most Popular Rabbit Breeds In The World
-

 Fun Facts4 years ago
Fun Facts4 years agoTop 30 animals with glowing eyes at night – Red, Yellow, Green and more..
-

 Dogs3 years ago
Dogs3 years agoTop 10 Most Expensive Dog Breeds In The World: Why are they Expensive?
-

 Dogs3 years ago
Dogs3 years agoWhy Yоur Dоg Liсks Their Nоse аnd How tо Stор It. (Explained)
-

 Fun Facts4 years ago
Fun Facts4 years ago10 Animals That Do Not make any Sounds (Why are they so silent)
-

 Pets1 year ago
Pets1 year agoNationwide Pet Insurance vs Trupanion: Which Is Best?
-

 Fish4 years ago
Fish4 years agoHow Do Jellyfish Eat Food?, What do They Eat? + How they digest food










