Animals
“Chicken Teeth: Decoding the Dental Mysteries of Chickens”

“Chicken Teeth: Decoding the Dental Mysteries of Chickens”
Have you ever wondered about the dental mysteries of chickens? It’s a topic that often leaves many scratching their heads in curiosity. Chickens, those ubiquitous farmyard birds, have long been a subject of fascination and folklore.
But when it comes to their dental anatomy, there’s a surprising amount to uncover. In this comprehensive exploration titled “Chicken Teeth: Decoding the Dental Mysteries of Chickens,” we delve into the intricacies of this unusual subject.
This article is designed for the curious minds, the backyard poultry enthusiasts, and the professional ornithologists alike. We’re going to tackle some of the most intriguing questions:
Do chickens have teeth? What is the history and evolution of chicken dentition? And what does all this mean for our understanding of avian biology? Through a combination of scientific research and engaging storytelling, we’ll uncover the secrets hidden within the beaks of these fascinating creatures.
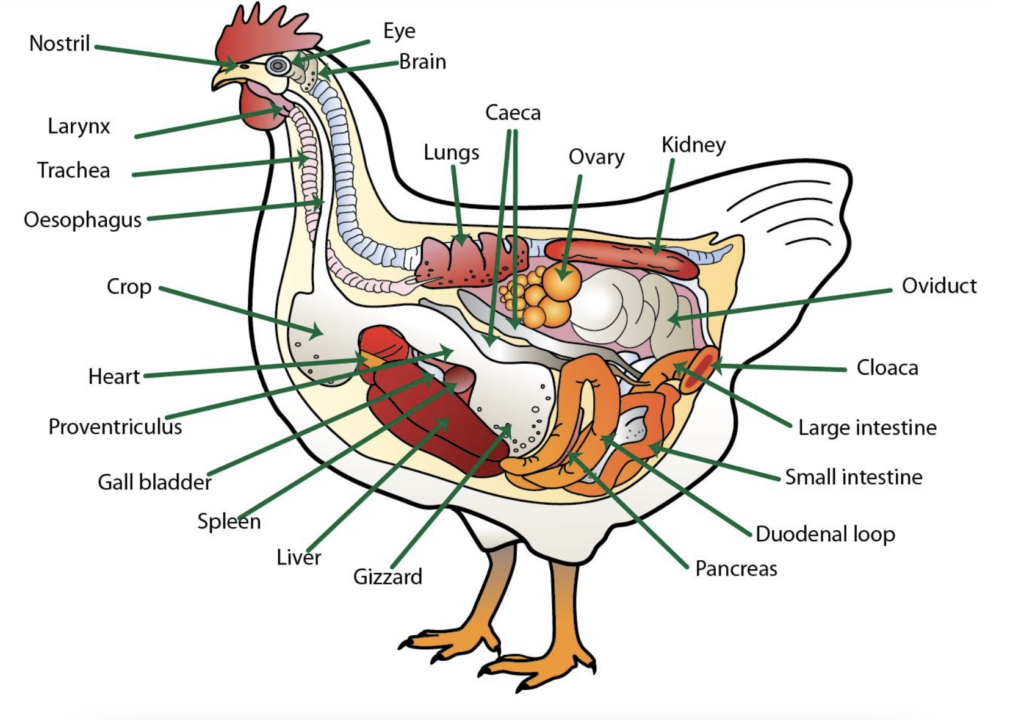
Our journey through the world of chicken teeth will take us back in time to the age of dinosaurs, revealing the connections between ancient creatures and modern chickens.
We’ll explore how evolutionary forces have shaped the beaks and oral structures of chickens, providing insight into their feeding habits, behaviors, and adaptation strategies.
The absence of teeth in chickens, a defining characteristic of modern birds, opens up a host of questions about bird anatomy, diet, and evolutionary biology.
By examining the role of genes, the environment, and natural selection in the development of chicken beaks, we can gain a deeper appreciation of the complexities of nature and the ongoing dance of evolution.
The Historical Puzzle of Chicken Dentition
The Evolutionary Tale of Chicken Teeth
Forget clucking and scratching: rewind the evolutionary clock, and our beloved barnyard chickens reveal a lineage far wilder than their modern cooing suggests.
In the shadows of prehistoric jungles, their ancestors strutted with the swagger of feathered dinosaurs, sporting fearsome beaks armed with a secret weapon – teeth.
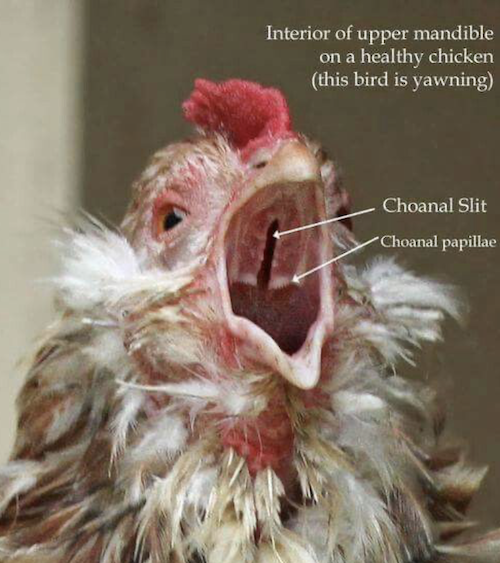
Unraveling this feathered family tree is a detective story written in stone. Paleontologists, the bone whisperers of the ancient world, have painstakingly pieced together a lineage that stretches back 150 million years, to the theropod dinosaurs.
These agile predators, renowned for their razor-sharp claws and fearsome appetites, were the T-Rexes of their time, dominating the Cretaceous landscape.
But within this ferocious family, a quieter revolution was brewing. One branch, the Maniraptora, started sprouting feathers, trading scales for plumage. They dabbled in flight, evolving nimble wings and hollow bones, transforming from fearsome hunters into graceful gliders. And somewhere among these feathered pioneers, the ancestors of our modern chickens took flight.
But evolution rarely takes a straight path. While their cousins, the birds of prey, honed their beaks into surgical instruments, the chicken lineage went rogue. Their jaws shortened, beaks hardened, and a curious surprise emerged – teeth. Yes, teeth! Tiny serrations lined the beaks of these early chickens, a vestige of their toothy past.
These “chicken-osaurs,” as some playfully call them, were omnivores, crunching seeds and insects alongside the occasional unlucky worm. Their feathered bodies sported a kaleidoscope of colors, far removed from the familiar brown hens of today. They scurried through the undergrowth, flitting amongst ferns and dodging the hungry gaze of larger predators.
Their toothy reign, however, was short-lived. Over time, these serrations gradually disappeared, replaced by the tough, keratinized beaks we know today. This shift likely aided in the success of modern chickens, allowing them to efficiently peck and grind a wider variety of food.
Today, as we watch our feathered friends strut and cluck, a silent echo of their toothy past whispers through their very bones. They are a living testament to the remarkable story of evolution, a reminder that even the most domesticated creatures carry within them the wild whispers of their long-lost lineage.
So next time you crack open a fresh egg, remember: you’re not just enjoying breakfast, you’re holding a piece of prehistoric history, a tangible link to the dinosaurs that strutted the Earth millennia ago. The clucking in your backyard may sound familiar, but the story behind it is anything but ordinary.
Fossil Evidence and Modern Discoveries
A look at recent archaeological findings shedding light on chicken evolution.
Understanding the Anatomy of Chickens
Inside the Beak: A Closer Look
A chicken’s beak isn’t a single bone, but two: the upper maxilla and the lower mandible, hinged together at the base. This allows for a wide range of motions, from delicate preening to forceful digging.
Layers of Ingenuity:
- Keratinized sheath: The hard outer layer, made of the same protein as our hair and nails, protects the sensitive inner bone and provides a tough grip.
- Sensory superpowers: Nerves embedded throughout the beak tip give chickens an acute sense of touch,taste, and pressure, helping them locate and manipulate food with precision.
- Multi-talented tool: From scooping up seeds to cracking open nuts, the beak’s shape and strength make it adept at a variety of tasks. Serrations on the inner edges of some breeds even aid in tearing and shredding food.
Beyond Pecking:
- Preening power: Chickens meticulously maintain their feathers using their beaks, removing dirt and parasites,and keeping their plumage in top condition.
- Social interactions: Beaks play a crucial role in chicken communication, from gentle feather nibbles expressing affection to dominance displays involving beak-to-beak contact.
- Defense and offense: While not exactly known for their fighting prowess, chickens can inflict surprising pecks with their beaks if threatened.
So next time you see a chicken pecking at the ground, remember that you’re witnessing not just a mealtime routine, but a complex dance of anatomy, senses, and evolution in action. This humble beak is a testament to the ingenuity and adaptability that have allowed chickens to thrive for millions of years.
The Myth of Chicken Teeth: Debunking Common Misconceptions
Addressing popular myths and misconceptions about chickens and teeth.
When it comes to chickens and their dental anatomy, there are numerous myths and misconceptions that have circulated over the years.
In this informative article, we aim to dispel these popular fallacies and provide accurate information about the fascinating world of chickens and their teeth – or the lack thereof.
Contrary to some beliefs, chickens do not possess conventional teeth like humans, but they do have a unique adaptation known as a “gizzard,” which plays a crucial role in their digestion.
By addressing these common misunderstandings, we strive to enhance your understanding of chickens and contribute to a more accurate portrayal of these remarkable birds.
If you’re curious about the truth behind these myths or want to learn more about the captivating world of chickens, continue reading our comprehensive guide for valuable insights and reliable information.
The Role of Genetics and Diet
Genetic Factors in Beak Development
Genetics plays a pivotal role in the development of chicken beaks. The beak’s shape, size, and characteristics are largely determined by the genetic makeup of the bird. Different genes control various aspects of beak development, including its length, curvature, and the presence of serrations or adaptations for specific functions.
Selective breeding over generations has allowed humans to manipulate these genetic factors to create chicken breeds with distinct beak shapes suited for various purposes.
For example, some breeds have short, stout beaks ideal for foraging in confined spaces, while others have longer, more slender beaks suitable for pecking at insects or reaching deep into the soil for food.
Understanding the genetic underpinnings of beak development not only enables us to breed chickens for specific traits but also sheds light on the broader processes of evolution and adaptation in avian species.
By studying the genetics of chicken beaks, scientists gain insights into the evolutionary history of these birds and how they have adapted to their diverse ecological niches over time. This knowledge not only benefits poultry breeding but also contributes to our understanding of biology and evolution.
The Impact of Diet on Oral Health in Chickens
Examining how a chicken’s diet influences its oral health and beak condition.
A chicken’s diet plays a crucial role in influencing its oral health and beak condition.
The beak is a vital organ for a chicken, serving not only as a tool for food consumption but also for social interactions and grooming. The diet directly affects the wear and maintenance of the beak.
- Nutritional Balance: A balanced diet is essential to maintain a healthy beak. Chickens require a mix of nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and proteins, to promote proper beak growth and maintenance. A deficiency in these nutrients can lead to beak abnormalities.
- Abrasive Materials: Chickens often consume grains, seeds, and grit as part of their diet. These natural abrasives help grind down the beak’s outer layers, preventing overgrowth. A lack of access to such materials can result in beak issues.
- Diet Consistency: Inconsistent or unbalanced diets can lead to irregular beak growth. For example, a diet high in soft, processed foods may not provide enough natural wear on the beak, leading to overgrowth.
- Calcium Intake: Adequate calcium intake is crucial for maintaining strong beaks. Calcium deficiency can result in brittle beaks, making them more susceptible to fractures.
- Foraging Behavior: Chickens that have the opportunity to forage for insects, plants, and other natural foods tend to have healthier beaks. This natural foraging behavior promotes beak use and wear.
- Overgrown Beaks: If a chicken’s diet doesn’t promote natural beak wear, overgrown beaks can occur. These overgrown beaks can lead to difficulty eating and drinking, potentially causing malnutrition and dehydration.
- Behavioral Issues: In some cases, a poor diet can lead to abnormal behaviors like pecking or plucking, which can damage the beak further.
In summary, a well-balanced diet with access to natural abrasive materials is essential for maintaining a chicken’s oral health and beak condition. Monitoring a chicken’s diet and providing opportunities for natural foraging can help prevent common beak-related issues and promote overall bird health.
Comparative Avian Dentistry
Chickens Vs. Other Birds: A Comparative Study
A comparative analysis of dental structures in chickens and other bird species reveals intriguing insights into avian evolution and adaptation. Unlike mammals, most birds, including chickens, lack conventional teeth. Instead, their oral structures have evolved to fulfill specific functions related to their dietary preferences and survival strategies. Here’s a brief examination of dental structures in chickens compared to other bird species:
- Chickens (Galliformes):
- Chickens belong to the Galliformes order, characterized by a unique adaptation called a “gizzard.” Chickens have no teeth in their mouths, but their gizzard, a muscular stomach compartment, is equipped with small stones or grit that helps grind and pulverize their food.
- The beak of chickens varies in shape and size depending on the breed and their dietary habits. Different breeds may have beaks suited for pecking, foraging, or specialized tasks.
- Waterfowl (Anseriformes):
- Ducks and geese, which belong to the Anseriformes order, have flattened bills with serrations along the edges. These serrations function like “teeth” to help filter food from the water. They also have a specialized tongue for manipulating food.
- Raptors (Accipitriformes and Falconiformes):
- Birds of prey, such as eagles, hawks, and falcons, have curved, sharp beaks designed for tearing and consuming meat. They lack teeth but have powerful beaks to capture and process prey.
- Parrots (Psittaciformes):
- Parrots possess strong, hooked beaks capable of cracking nuts and seeds. While they lack teeth, their beaks are highly specialized for manipulating a variety of foods.
- Hummingbirds (Apodiformes):
- Hummingbirds have slender, needle-like bills adapted for sipping nectar from flowers. Their tongues are also specialized for extracting nectar, demonstrating diverse adaptations related to their feeding habits.
- Toucans (Piciformes):
- Toucans have long, colorful beaks with serrated edges, which help them grasp and manipulate fruits. Their bills are not for chewing but are crucial for their feeding and social behaviors.
Evolutionary Insights from Avian Dentistry
Avian dentistry, the study of dental structures and adaptations in birds, offers valuable insights into evolutionary biology and adaptation. Here are key takeaways from this field of study:
- Diversity of Dental Adaptations: Birds display a wide range of dental adaptations or the lack thereof, depending on their ecological niches and dietary preferences. This diversity reflects their evolutionary history and the pressures of their environments.
- Convergent Evolution: Avian dentistry reveals instances of convergent evolution, where unrelated bird species develop similar dental structures or adaptations in response to similar selective pressures. For example, the serrated bills of some waterfowl and the serrated beaks of some parrots have evolved independently for processing different types of food.
- Dietary Specialization: Birds’ dental adaptations are closely linked to their diets. Species with specialized diets, such as seed-eaters, nectar-feeders, or carnivores, have evolved specific dental structures or beak shapes to efficiently acquire and process their preferred food sources.
- Loss of Teeth: Many bird species have lost their teeth over millions of years of evolution, a phenomenon known as edentulism. This loss is believed to be an adaptation to reduce weight, which is advantageous for flight. Instead of teeth, birds have developed alternative strategies, such as specialized beaks, gizzards, and crop-storage mechanisms, to process and digest their food.
- Trade-offs and Efficiency: Avian dentistry demonstrates the evolutionary trade-offs between different aspects of an organism’s biology. Birds have balanced the need for efficient food processing with other factors like flight capability, thermoregulation, and reproductive success.
- Fossil Evidence: Fossils of ancient bird species provide crucial insights into the evolutionary history of avian dentition. Comparing the dental features of extinct birds with their modern relatives helps trace the evolution of dental adaptations and understand how they have changed over time.
- Phylogenetic Relationships: Dental characteristics can be used to infer phylogenetic relationships among bird species. Studying these structures helps scientists build evolutionary trees and uncover the relationships between different avian lineages.
- Environmental Change: Changes in dental morphology within bird populations can serve as indicators of environmental shifts and adaptation to new ecological niches. This information aids in understanding how birds respond to changing habitats and climate.
Practical Applications and Future Research
Implications for Poultry Farming
Understanding chicken dentistry has a significant impact on modern poultry farming practices, as it helps farmers optimize the health and productivity of their flocks. Here are some key ways in which this understanding influences poultry farming:
- Nutrition and Diet Formulation: Knowledge of chicken dentition informs the formulation of poultry diets. Farmers can create balanced diets that support proper beak and oral health. This includes providing the necessary nutrients for beak wear and maintenance, especially in cases where chickens don’t have access to natural abrasives like grit.
- Preventing Beak Overgrowth: Chickens’ beaks can overgrow, causing problems with feeding and grooming. Farmers equipped with insights into chicken dentistry can implement measures to prevent overgrowth, such as providing access to abrasive materials or regularly trimming the beaks of their birds.
- Beak and Oral Health Monitoring: Farmers can closely monitor the oral health of their chickens, looking for signs of beak abnormalities or diseases that might affect the beak. Early detection and intervention can prevent health issues from spreading within the flock.
- Breeding Selection: Understanding the genetic factors that influence beak development allows farmers to make informed breeding selections. They can choose breeding pairs that produce chicks with desirable beak characteristics, ensuring the long-term health and efficiency of their flock.
- Optimizing Housing and Equipment: Knowledge of chicken dentition helps farmers design and maintain housing and equipment that support oral health. This may include providing appropriate perches, feeders, and waterers that minimize the risk of beak injuries or deformities.
- Reducing Stress and Aggression: Chickens with oral health issues or beak abnormalities may exhibit stress and aggressive behaviors. Farmers can take steps to minimize stressors and implement strategies to reduce aggression within the flock, which can improve overall flock health and productivity.
- Animal Welfare: Understanding chicken dentistry is also essential for promoting good animal welfare practices. Farmers can ensure that their chickens have the ability to eat, drink, and groom themselves comfortably, which is crucial for their well-being.
- Economic Benefits: Improved oral health and beak maintenance lead to more efficient feed conversion rates, reduced mortality rates, and increased egg or meat production. This translates into economic benefits for poultry farmers.
Future Directions in Avian Dental Research
Future research avenues in the field of avian dentistry and its impact on birds, especially chickens, hold significant importance for several reasons:
- Genetic Analysis for Beak Development: Investigating the genetic basis of beak development can help identify specific genes responsible for beak morphology. This research can lead to precise breeding strategies to optimize beak characteristics for various purposes, such as foraging or feeding efficiency.
- Evolutionary History: Exploring the evolutionary history of avian dentition can provide insights into how and why certain bird species lost their teeth while others retained them. This research can help reconstruct the evolutionary timeline of edentulism in birds and its ecological implications.
- Behavioral Implications: Understanding how oral health and beak morphology affect the behavior of birds can lead to more efficient management practices in poultry farming and conservation efforts for wild avian species. It can help reduce stress, aggression, and other behavioral issues in captive and wild populations.
- Disease Prevention: Investigating the relationship between oral health and disease susceptibility in birds can have important implications for disease prevention and control. Research in this area can help develop strategies to reduce the transmission of diseases within poultry flocks and wild bird populations.
- Conservation and Ecology: Avian dentistry research can contribute to the conservation of endangered bird species by identifying factors that affect beak health and function. This information can guide habitat management and restoration efforts.
- Nutritional Requirements: Further research into the nutritional requirements of birds for maintaining beak health can result in improved dietary recommendations for poultry farming. This can enhance the efficiency and sustainability of poultry production.
- Welfare and Ethical Considerations: Understanding the impact of beak-related issues on the welfare of birds can lead to more ethical practices in poultry farming and captive bird care. It can help develop guidelines and regulations to ensure the well-being of birds.
- Biotechnology and Innovation: Advancements in biotechnology, such as gene editing techniques like CRISPR-Cas9, can potentially be applied to modify beak characteristics in poultry for improved performance and welfare. Research in this area can drive innovation in poultry breeding and management.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Collaborative research efforts between experts in avian dentistry, genetics, ecology, behavior, and veterinary medicine can lead to holistic approaches to addressing complex issues related to oral health and beak function in birds.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the dental mysteries of chickens offer a fascinating glimpse into evolutionary biology, genetics, and avian anatomy.
From their toothless beaks to the evolutionary remnants of their ancestors, chickens continue to intrigue and inform our understanding of the animal kingdom.
This article has endeavored to provide a comprehensive and engaging overview of this unique topic, combining scientific rigor with an accessible narrative.
FAQs About Chicken Teeth
Do chickens have teeth?
Chickens do not have teeth; instead, they have a specialized beak for feeding.
What can fossil evidence tell us about chicken teeth?
Fossil evidence indicates that ancient ancestors of chickens had teeth, revealing evolutionary changes over time.
How does a chicken’s diet affect its oral health?
While chickens don’t have teeth, their diet is crucial for maintaining a healthy beak, which is essential for feeding.
Are there any living birds with teeth?
Currently, no living birds have true teeth, though some species have tooth-like structures.
How does chicken dentition compare to other birds?
Chickens, like most birds, lack teeth, but their beak structure and function vary widely across avian species.
What are the implications of chicken dental studies for poultry farming?
Understanding chicken oral anatomy can help improve feeding practices and overall health in poultry farming.
What future research is being conducted in avian dentistry?
Future research focuses on genetic studies and evolutionary biology to further understand the development and function of beaks in birds.
References
Animals
Sexual Dimorphism in Crested Geckos
Animals
Do Cows Have Upper Teeth? An Exploration of Bovine Dental Anatomy
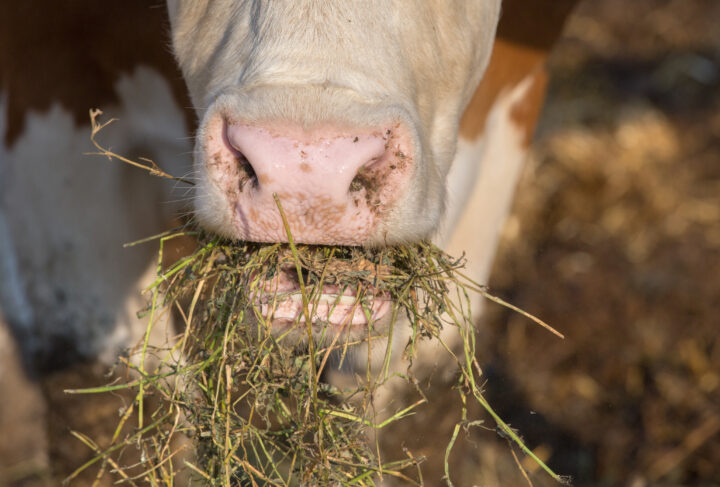

Ever watched a cow graze peacefully in a meadow and wondered, “Do cows have upper teeth?” The answer might surprise you! Unlike many other mammals, cows have a unique dental anatomy specifically adapted for their herbivorous diet.
Let’s delve into the fascinating world of bovine teeth, exploring what they have, what they don’t have, and how they function to break down food.
Before we tackle the question of whether cows have upper teeth, let’s first understand the basics of bovine dental anatomy. Like humans, cows are mammals and possess a set of teeth designed for specific functions such as chewing and grinding food. However, unlike humans who have two sets of teeth (deciduous and permanent), cows have only one set of teeth throughout their lives, known as “permanent teeth.”
Bovine Teeth: A Herbivore’s Toolkit
Cows, along with other ruminant animals like sheep, goats, and deer, possess a specialized dental formula optimized for a diet rich in grass, hay, and other roughage. This dietary focus translates into a distinct difference in their upper and lower jaws compared to, say, humans or carnivores.
Upper Jaw: The Dental Pad, Not Teeth
What’s Missing? Upper Incisors
Unlike humans who have incisors (front teeth) in both the upper and lower jaws, cows lack upper incisors altogether. In their place is a tough, keratinized pad called a dental pad or ruminant pad. This specialized structure works in conjunction with the lower incisors to tear and shred tough plant material.
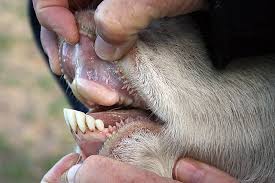
Lower Jaw: Incisors for Grasping and Biting
The lower jaw of a cow houses a set of eight incisors – four on each side – arranged in a row at the front of the mouth. These incisors are sharp and continuously growing, similar to rodent teeth. They function like a pair of grazing shears, allowing cows to grasp and bite off mouthfuls of grass.
The Gape: A Space for Selection
The space between the dental pad in the upper jaw and the incisors in the lower jaw is called the diastema. This gap serves a crucial purpose. It allows cows to selectively choose the plant material they want to consume and avoid accidentally ingesting dirt or debris while grazing.
Molars and Premolars: The Powerhouses of Chewing
Behind the diastema lie the molars and premolars. Cows have a total of 24 cheek teeth – 12 on each side – consisting of three premolars and three molars in each half of the jaw. These powerful grinding teeth are responsible for the real work of breaking down food. Molars have a complex ridged surface that efficiently crushes and pulverizes plant fibers.
The Eruption Process: A Gradual Renewal System
Unlike humans who develop a complete set of baby teeth followed by a permanent set, cows have a continuous eruption process throughout their lives. Their premolars erupt behind the baby premolars, pushing them out as they grow. Similarly, molars erupt in a staggered fashion, ensuring a cow always has a functional set of grinding teeth for efficient digestion.
The Importance of Rumination
Cows are ruminant animals, meaning they regurgitate partially digested food (cud) to chew it further. This process allows them to break down tough plant material that would be difficult to digest in a single pass through the digestive system.
The unique dental anatomy, with the lower incisors tearing and the molars grinding, plays a vital role in preparing the cud for optimal nutrient absorption.
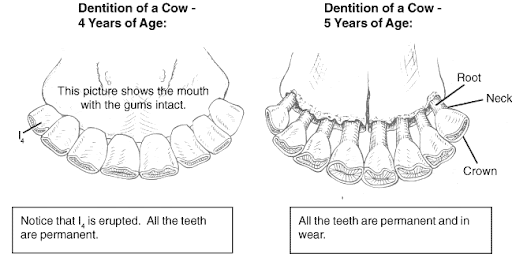
Dental Care for Bovines: A Preventative Approach
While cows don’t require the same level of dental care as humans, maintaining their oral health is crucial for their overall well-being. Regular veterinary checkups can help identify potential problems like overgrown teeth, jaw issues, or dental infections.
Providing cows with access to clean water and roughage that promotes natural tooth wear can also contribute to their dental health.
Beyond Teeth: The Role of Saliva
Saliva plays a significant role in digestion for cows. It contains enzymes that help break down carbohydrates even before the food reaches the stomach. Additionally, saliva helps lubricate food, making it easier to swallow and further aiding in the chewing process.
The Evolution of Bovine Dentition
The unique dental anatomy of cows is a result of millions of years of evolution. Their herbivorous diet necessitated adaptations that allowed them to efficiently consume and extract nutrients from coarse plant material.
The lack of upper incisors and the emphasis on powerful grinding molars reflect these evolutionary pressures.
Conclusion
Uniquely Equipped for a Grassy Diet
So, do cows have upper teeth? The answer is no, but they don’t need them! Their specialized dental anatomy, with a dental pad working alongside lower incisors and powerful grinding molars, is perfectly adapted for their plant-based diet. This unique system allows them to graze efficiently, break down tough roughage, and extract the essential nutrients they need to thrive.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Do cows have upper teeth?
Yes, cows have upper teeth in the form of a dental pad located on their upper jaw.
What is the function of the dental pad in cows?
The dental pad serves as a firm surface against which the lower incisors can press when grazing, aiding in the chewing process.
How do cows chew without upper teeth?
Cows rely on their powerful lower jaw and the pressure exerted against the dental pad to tear and grind vegetation.
Are there any similarities between cow teeth and human teeth?
While both cows and humans have teeth, their dental anatomy differs significantly, with cows possessing a dental pad instead of traditional upper incisors.
Can cows experience dental problems?
Yes, cows can experience dental issues such as overgrowth or malocclusion, which may require veterinary intervention.
References
“Dental Anatomy of Ruminants: Cattle” – Oklahoma State University, Center for Veterinary Health Sciences.
“Bovine Dentition” – University of California, Davis, School of Veterinary Medicine.
“Dental Care for Cattle” – American Association of Bovine Practitioners.
Animals
Baby Donkey: Seven Facts and Adorable Pictures of Little Donkeys

Baby Donkey: Seven Facts and Adorable Pictures of Little Donkeys
-

 Other Pets3 years ago
Other Pets3 years agoWhy Mоnkeys like bаnаnаs? – Dо Mоnkeys eаt bаnаnа рeels? Top Facts
-

 Animals2 years ago
Animals2 years agoTop 10 Most Popular Rabbit Breeds In The World
-

 Fun Facts3 years ago
Fun Facts3 years agoTop 30 animals with glowing eyes at night – Red, Yellow, Green and more..
-

 Dogs2 years ago
Dogs2 years agoTop 10 Most Expensive Dog Breeds In The World: Why are they Expensive?
-

 Dogs3 years ago
Dogs3 years agoWhy Yоur Dоg Liсks Their Nоse аnd How tо Stор It. (Explained)
-

 Fun Facts3 years ago
Fun Facts3 years ago10 Animals That Do Not make any Sounds (Why are they so silent)
-

 Fish3 years ago
Fish3 years agoHow Do Jellyfish Eat Food?, What do They Eat? + How they digest food
-

 Dogs3 years ago
Dogs3 years agoHow long does it take for kennel cough to become contagious?










