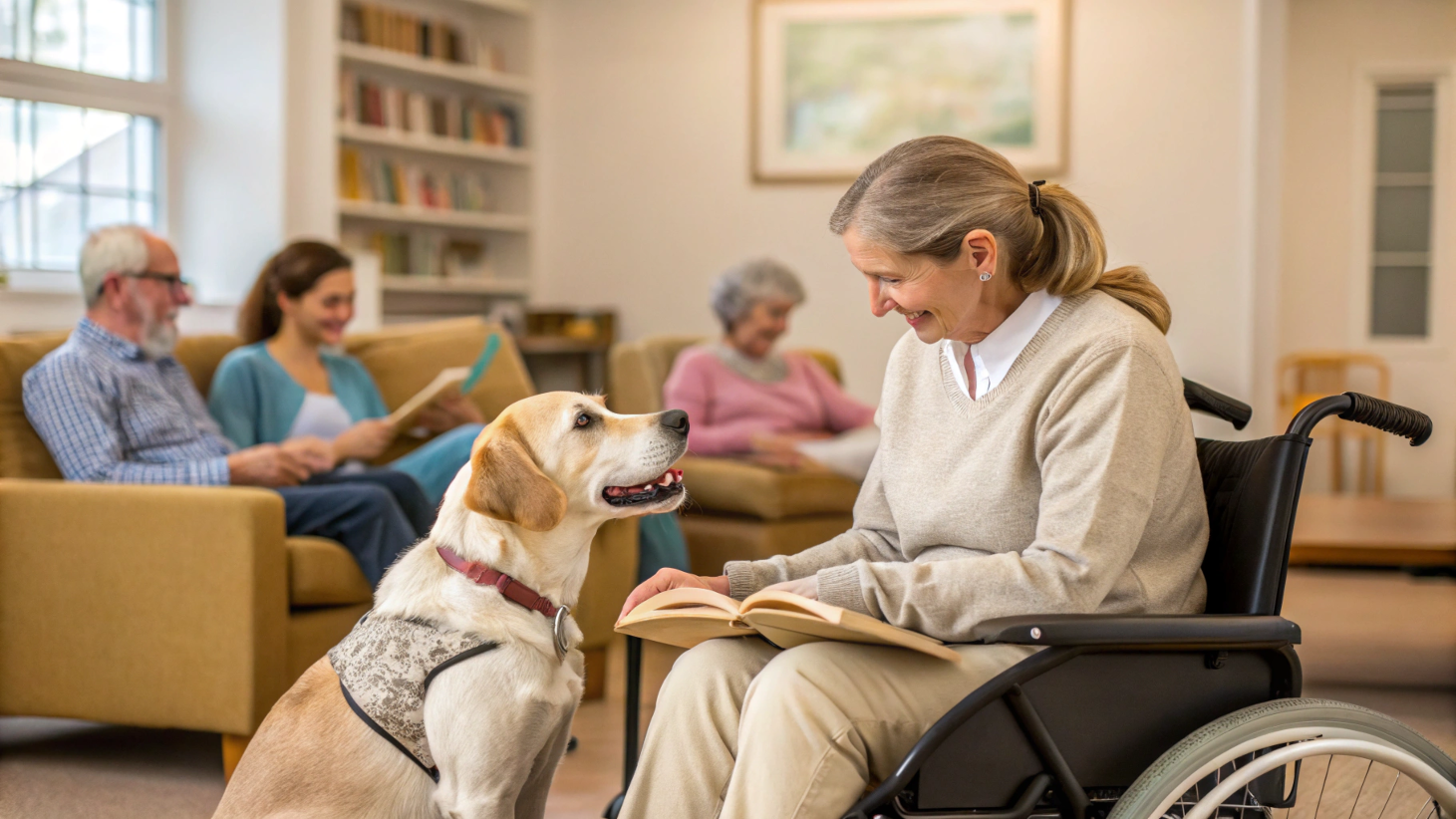
In recent years, the therapeutic potential of the human-animal bond has gained significant recognition, leading to the rise of animal-assisted therapy (AAT) as a valuable form of treatment. Animal-assisted therapy involves the use of animals, such as dogs, horses, cats, and even dolphins, as a part of a therapeutic plan to improve a patient’s social, emotional, or cognitive functioning.
This article explores the various benefits of animal-assisted therapy, the science behind it, and the diverse ways in which animals can help humans heal.
What is Animal-Assisted Therapy?
Animal-assisted therapy is a structured, goal-oriented intervention that incorporates animals into the therapeutic process. Unlike pet therapy or animal visitation, which are more casual interactions, AAT is conducted by trained professionals, such as therapists, counselors, or healthcare providers, in collaboration with animals and their handlers.
Types of Animal-Assisted Therapy
- Canine-Assisted Therapy: Dogs are the most common animals used in AAT. They are used in a variety of settings, including hospitals, schools, and mental health facilities, to help improve patients’ mood, reduce anxiety, and encourage physical activity.
- Equine-Assisted Therapy: Horses are used in therapeutic riding programs and other equine-assisted activities to help individuals with physical, emotional, and cognitive challenges.
- Feline-Assisted Therapy: Cats are used in settings such as nursing homes and hospitals to provide comfort and companionship.
- Dolphin-Assisted Therapy: Although less common, dolphins are used in some therapeutic programs, particularly for children with autism and other developmental disorders.
The Benefits of Animal-Assisted Therapy
1. Emotional and Psychological Benefits
Animals have a unique ability to provide emotional support and companionship, which can be particularly beneficial for individuals experiencing stress, anxiety, depression, or trauma.
Case Study: Veterans with PTSD
Animal-assisted therapy has been shown to be effective in helping veterans with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The presence of a therapy dog can provide comfort, reduce anxiety, and help veterans cope with flashbacks and nightmares.
2. Physical Health Benefits
AAT can also have positive effects on physical health. Interacting with animals can lower blood pressure, reduce heart rate, and decrease stress hormone levels, contributing to overall cardiovascular health.
Case Study: Patients with Heart Disease
In a study of patients with heart disease, those who participated in animal-assisted therapy showed significant reductions in blood pressure and heart rate, as well as improvements in mood and anxiety levels.
3. Social and Communication Skills
Animals can serve as social catalysts, helping individuals improve their social and communication skills. For example, children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) often find it easier to interact with animals than with humans, which can lead to improvements in their social interactions.
Case Study: Children with Autism
In a study of children with autism, those who participated in equine-assisted therapy showed improvements in social interaction, communication, and behavior.
4. Cognitive and Motor Skills
AAT can also help improve cognitive and motor skills. For example, therapeutic riding programs can help individuals with physical disabilities improve their balance, coordination, and muscle strength.
Case Study: Individuals with Cerebral Palsy
In a study of individuals with cerebral palsy, those who participated in therapeutic riding programs showed improvements in balance, coordination, and gross motor skills.
5. Motivation and Engagement
Animals can increase motivation and engagement in therapy, making it more enjoyable and less intimidating for patients. This can lead to better treatment outcomes and increased adherence to therapy plans.
Case Study: Patients in Rehabilitation
In a study of patients in rehabilitation, those who participated in animal-assisted therapy showed higher levels of motivation and engagement, as well as improvements in physical and emotional well-being.
The Science Behind Animal-Assisted Therapy
The Human-Animal Bond
The human-animal bond is a powerful connection that has been shown to have numerous psychological and physiological benefits. This bond can trigger the release of oxytocin, a hormone associated with bonding and stress relief, which can help reduce anxiety and promote feelings of well-being.
Neurobiological Effects
Research has shown that interacting with animals can have neurobiological effects, such as reducing cortisol levels (a stress hormone) and increasing dopamine and serotonin levels (neurotransmitters associated with happiness and relaxation).
Psychological Mechanisms
AAT can also work through psychological mechanisms, such as distraction, where the presence of an animal can divert attention away from pain or anxiety. Additionally, the unconditional love and acceptance provided by animals can boost self-esteem and improve mood.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the difference between animal-assisted therapy and pet therapy?
Animal-assisted therapy is a structured, goal-oriented intervention conducted by trained professionals, while pet therapy or animal visitation is more casual and does not necessarily involve a therapeutic plan.
2. What types of animals are used in animal-assisted therapy?
Common animals used in AAT include dogs, horses, cats, and dolphins. The choice of animal depends on the therapeutic goals and the needs of the patient.
3. Who can benefit from animal-assisted therapy?
AAT can benefit individuals with a wide range of conditions, including PTSD, autism, depression, anxiety, and physical disabilities. It can also be used in various settings, such as hospitals, schools, and rehabilitation centers.
4. Is animal-assisted therapy safe?
Yes, AAT is generally safe when conducted by trained professionals. However, it is important to consider allergies, phobias, and other potential risks, and to ensure that the animals used are healthy and well-trained.
5. How can I find an animal-assisted therapy program?
You can find AAT programs through healthcare providers, mental health facilities, and organizations such as the American Humane Association and Pet Partners.
Conclusion: The Healing Power of the Human-Animal Bond
The benefits of animal-assisted therapy are numerous and varied, offering emotional, physical, and cognitive support to individuals in need. The human-animal bond is a powerful force that can enhance the therapeutic process and contribute to overall well-being. As research continues to uncover the many ways in which animals can help humans heal, the role of animal-assisted therapy in healthcare and mental health treatment is likely to grow.
References
1.O’Haire, M. E., et al. (2015). “Animal-Assisted Intervention for Trauma: A Systematic Review.” Frontiers in Psychology, 6, 1121.
2.Cole, K. M., et al. (2007). “Animal-Assisted Therapy in Patients Hospitalized with Heart Failure.” American Journal of Critical Care, 16(6), 575-585.
3.Gabriels, R. L., et al. (2012). “Pilot Study Measuring the Effects of Therapeutic Horseback Riding on School-Age Children and Adolescents with Autism Spectrum Disorders.” Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 42(1), 1-12.
4.Ziviani, J., et al. (2010). “The Effect of Therapeutic Horseback Riding on the Physical Function of Children with Cerebral Palsy.” Pediatric Physical Therapy, 22(3), 322-330.
5.Berget, B., & Grepperud, S. (2011). “Animal-Assisted Therapy: Effects on Pain and Motivation in Rehabilitation.” Journal of Rehabilitation Research and Development, 48(4), 387-395.
Links
Post Views: 1,879