Animals
Squirrel Teeth: Everything You Need to Know About Squirrel Dental Health

Squirrel Teeth: Everything You Need to Know About Squirrel Dental Health
Squirrels, those delightful acrobats of the tree canopy, are known for their adorable antics and bushy tails. But have you ever paused to ponder over their dental health? Probably not. However, squirrel teeth play a vital role in their survival and well-being.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of squirrel dental health, exploring everything from their unique dental structure to common dental issues and how to keep those tiny comperes in top condition.
In this expansive and enlightening guide, we embark on a journey deep into the realm of squirrel dental health. Our exploration traverses the vast landscape of their unique dental structure, unveiling the marvels of evolution that equip these tiny choppers for their vital tasks.
From the razor-sharp incisors at the forefront of their mouths to the robust molars nestled towards the back, we unravel the intricacies of squirrel dentition, shedding light on their remarkable adaptation for a life spent foraging amidst the branches.
Yet, our odyssey does not end merely with admiration for their dental prowess. Instead, we venture further into the realm of potential challenges, delving into the realm of common dental issues that can afflict our furry friends.
From the specter of overgrown incisors to the complexities of malocclusion, we confront the realities that may compromise the dental health of these arboreal creatures.
But fear not, dear reader, for our mission is not one of despair but of empowerment. Armed with knowledge, we equip ourselves with the tools necessary to safeguard the dental well-being of our squirrel companions.
Through practical tips and expert guidance, we uncover the secrets to maintaining those tiny choppers in peak condition, ensuring our furry friends can continue their frolics amidst the treetops with unabated joy.
So, join us as we embark on this illuminating expedition into the world of squirrel dental health, where each word serves as a beacon illuminating the path towards a deeper understanding of these enchanting creatures and the vital role their teeth play in their lives.
Understanding Squirrel Dental Anatomy
Squirrel teeth are fascinating marvels of nature. Unlike humans, who have two sets of teeth (deciduous and permanent), squirrels have only one set of teeth that continuously grow throughout their lives.
This unique dental arrangement serves as a testament to the remarkable evolutionary strategies of these arboreal creatures. Unlike humans, who replace their teeth as they mature from infancy to adulthood, squirrels rely on a single set of teeth to meet all their dental needs.
This perpetual growth mechanism is essential for their survival, enabling them to maintain functional teeth even in the face of wear and tear from their voracious chewing habits.
These teeth are categorized into two main types:
Incisors:
- Positioned at the front of the mouth, incisors are sharp, chisel-like teeth used for gnawing and cutting through various materials, including nuts, seeds, and bark.
- Squirrel incisors have enamel only on the front surface, which keeps the cutting edge sharp and efficient.

Cheek Teeth (Molars and Premolars):
- Located towards the back of the mouth, these teeth are used for grinding and chewing food.
- Squirrels have molars and premolars that are adept at crushing hard substances like nuts and seeds.
The Importance of Squirrel Dental Health
Healthy teeth are crucial for a squirrel’s survival. Here’s why:
Nutrition:
Proper dental function allows squirrels to effectively break down and digest their food, ensuring they receive essential nutrients for energy and growth.
Foraging:
Squirrels rely on their teeth to crack open nuts, seeds, and other food sources found in their environment. Without healthy teeth, foraging becomes challenging, impacting their ability to find sustenance.
Defense:
In the wild, sharp teeth are not just for eating. Squirrels may use their incisors for self-defense, warding off predators or rival squirrels.
Common Dental Issues in Squirrels
While squirrel teeth are designed for durability, they are not immune to dental problems. Some common issues include:
Overgrowth:
- Due to the continuous growth of their teeth, squirrels are prone to overgrown incisors, which can interfere with eating and cause discomfort.
- Overgrown teeth may result from improper wear or underlying health issues.

Malocclusion:
- Malocclusion refers to misalignment of the teeth, where the upper and lower teeth do not meet properly.
- This condition can lead to difficulty eating and may require veterinary intervention to correct.
Dental Trauma:
- Squirrels are agile creatures, but accidents can happen. Falls or collisions with objects may result in dental trauma, such as chipped or fractured teeth.
- Dental trauma can cause pain and impair the squirrel’s ability to feed, necessitating prompt attention.
Maintaining Squirrel Dental Health
Keeping your furry friends’ teeth in tip-top shape is essential for their well-being. Here are some tips for maintaining squirrel dental health:
Provide Proper Nutrition:
- Offer a balanced diet rich in nuts, seeds, fruits, and vegetables to ensure adequate nutrition for dental health.
- Avoid feeding sugary or sticky treats, as they can contribute to dental decay.
Encourage Gnawing Behavior:
- Squirrels naturally gnaw on objects to wear down their teeth. Provide chew toys or branches for them to gnaw on, helping to prevent overgrowth.
Regular Veterinary Check-ups:
- Schedule routine check-ups with a qualified veterinarian familiar with exotic pets like squirrels.
- Veterinary professionals can assess dental health and provide guidance on preventive care and treatment options.
Conclusion
In conclusion, squirrel dental health is a critical aspect of their overall well-being. By understanding the unique anatomy of squirrel teeth, recognizing common dental issues, and implementing preventive measures, we can ensure our furry friends enjoy happy and healthy lives amidst the treetops.
FAQs About Squirrel Dental Health
How often should I check my squirrel’s teeth?
- It’s recommended to monitor your squirrel’s teeth regularly, ideally during daily interactions. Look for signs of overgrowth, malocclusion, or other abnormalities.
Can I trim my squirrel’s teeth at home?
- Trimming squirrel teeth is best left to experienced professionals, such as veterinarians familiar with exotic animal care. Attempting to trim teeth at home can cause injury and should be avoided.
What should I do if I notice signs of dental problems in my squirrel?
- If you observe any concerning changes in your squirrel’s dental health, such as overgrown or misaligned teeth, consult a veterinarian promptly. Early intervention can prevent further complications.
Are there specific foods that promote squirrel dental health?
- Providing a varied diet that includes hard foods like nuts and seeds can help promote natural wear of squirrel teeth. Additionally, offering chew toys or branches encourages gnawing behavior, which aids in dental maintenance.
Can dental issues in squirrels be prevented?
- While some dental issues may arise due to genetic factors or accidents, many can be prevented through proper nutrition, environmental enrichment, and regular veterinary care.
Are there any signs of dental problems I should watch for?
- Signs of dental issues in squirrels may include difficulty eating, excessive drooling, weight loss, reluctance to chew, or visible abnormalities in the teeth or mouth.
Is anesthesia necessary for squirrel dental procedures?
- Anesthesia is typically required for dental procedures in squirrels to ensure their safety and comfort. Veterinarians will assess the need for anesthesia based on the specific procedure and the squirrel’s health status.
References:
- Smith, J. (2019). “Squirrel Dental Care: Tips for Keeping Your Pet’s Teeth Healthy.” Exotic Pet Vet Clinic.
- Jones, L. (2021). “Understanding Squirrel Dentition: An Overview.” Journal of Exotic Animal Medicine, 10(2), 45-58.
- Wildlife Rehabilitation Center. (n.d.). “Common Dental Problems in Squirrels: A Guide for Rehabilitators.” Wildlife Rehabilitation Center Resources.
Animals
The Ethics of Animal Testing: Navigating the Complex Intersection of Science and Compassion
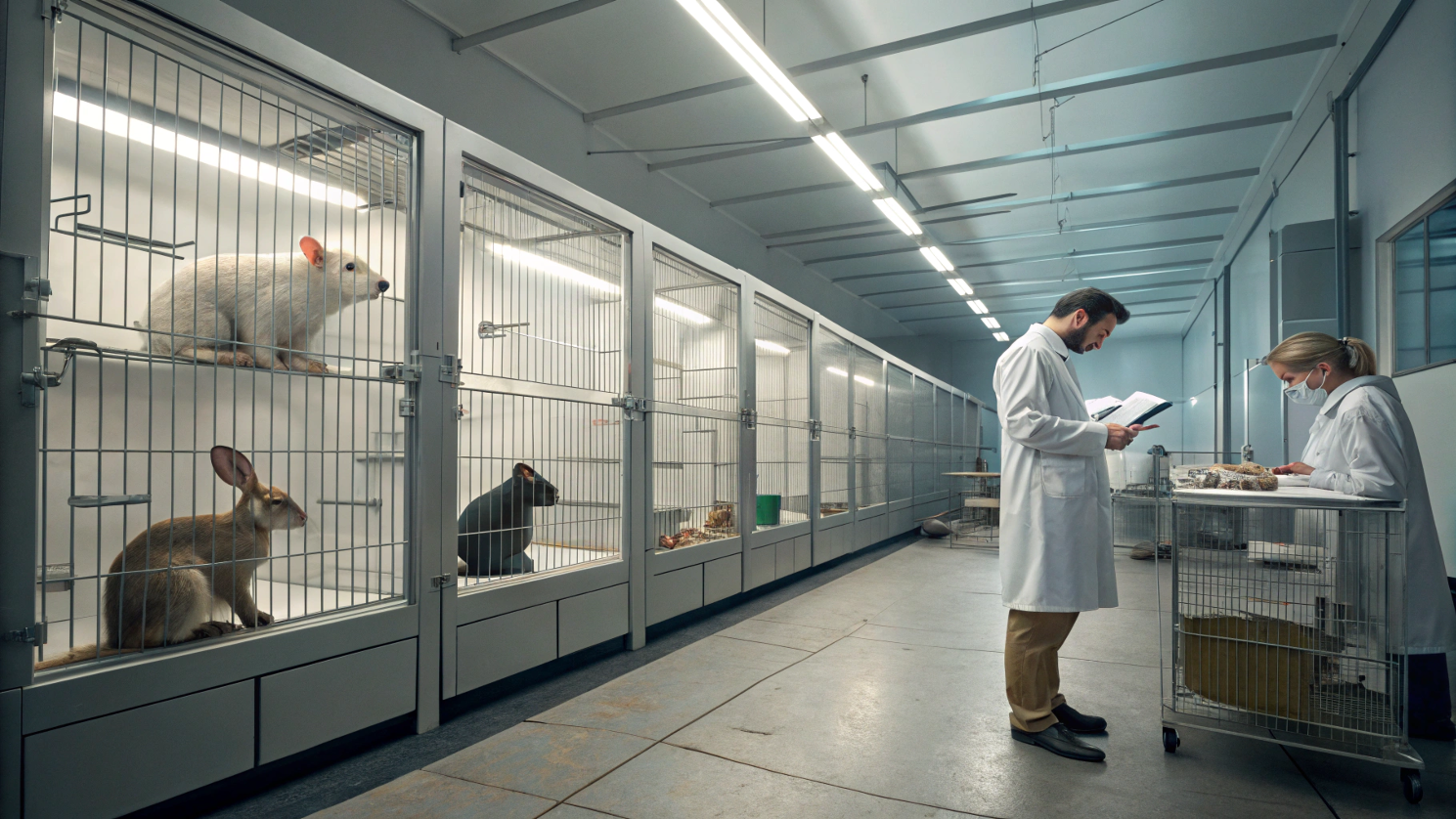

Animal testing has long been a contentious issue, sparking debates that span scientific, ethical, and philosophical domains. On one hand, animal testing has played a crucial role in advancing medical research, leading to breakthroughs in the treatment of diseases, the development of new drugs, and the understanding of biological processes.
On the other hand, the use of animals in experiments raises significant ethical concerns about animal welfare, the moral implications of causing suffering, and the validity of extrapolating results from animals to humans.
This article delves into the ethics of animal testing, exploring the arguments for and against it, the current state of regulations, and the ongoing quest to find alternatives that balance scientific progress with compassion for animals.
The Role of Animal Testing in Science
Historical Contributions
Animal testing has been instrumental in numerous scientific advancements. For instance, the development of vaccines for diseases such as polio and rabies relied heavily on animal experiments. Similarly, the discovery of insulin and the development of antibiotics were made possible through research involving animals.
Current Applications
Today, animal testing is used in a variety of fields, including:
- Medical Research: Testing new drugs, treatments, and surgical procedures.
- Toxicology: Assessing the safety of chemicals, cosmetics, and other products.
- Basic Science: Understanding biological processes and disease mechanisms.
Case Study: The Development of the Polio Vaccine
The development of the polio vaccine in the mid-20th century is a prime example of the importance of animal testing. Researchers used monkeys and mice to test the safety and efficacy of the vaccine before it was administered to humans, leading to the eventual eradication of polio in many parts of the world.
The Ethical Debate
Arguments in Favor of Animal Testing
Arguments Against Animal Testing
Case Study: The Thalidomide Tragedy
The thalidomide tragedy is a stark example of the limitations of animal testing. Thalidomide was tested on animals and deemed safe, but it caused thousands of birth defects in humans. This case highlights the potential for discrepancies between animal and human responses to drugs.
Current Regulations and Ethical Guidelines
International and National Regulations
Animal testing is subject to regulations and guidelines that vary by country. In the United States, the Animal Welfare Act and the Public Health Service Policy on Humane Care and Use of Laboratory Animals provide a framework for the ethical treatment of animals in research. The European Union has implemented the Directive 2010/63/EU, which sets strict standards for animal testing and promotes the use of alternatives.
The 3Rs Principle
The 3Rs principle—Replacement, Reduction, and Refinement—is a cornerstone of ethical animal testing. It advocates for:
- Replacement: Using alternative methods, such as computer modeling and in vitro studies, to replace animal testing.
- Reduction: Minimizing the number of animals used in experiments.
- Refinement: Improving experimental procedures to minimize pain and distress.
The Quest for Alternatives
In Vitro and In Silico Methods
Advances in technology have led to the development of alternative methods that reduce or eliminate the need for animal testing. In vitro methods, such as cell cultures and tissue engineering, allow researchers to study biological processes without using animals. In silico methods, such as computer modeling and simulation, provide tools for predicting the effects of drugs and chemicals.
Case Study: The Human-on-a-Chip
The “human-on-a-chip” is an innovative technology that uses microfluidic devices to mimic human organ systems. This technology has the potential to revolutionize drug testing by providing more accurate and ethical alternatives to animal models.
Public and Scientific Opinion
Public opinion on animal testing is divided, with many people calling for stricter regulations and the development of alternatives. Within the scientific community, there is growing interest in finding alternatives to animal testing, driven by ethical concerns and the limitations of animal models.
Conclusion: Striking a Balance
The ethics of animal testing is a complex and multifaceted issue that requires a delicate balance between scientific progress and compassion for animals. While animal testing has contributed to significant advancements in science and medicine, it is crucial to continue exploring and implementing alternatives that minimize animal suffering and address the ethical concerns surrounding the use of animals in research.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is animal testing?
Animal testing, also known as animal experimentation, is the use of animals in scientific research to study biological processes, test the safety and efficacy of drugs and chemicals, and develop new medical treatments.
2. Why is animal testing controversial?
Animal testing is controversial because it raises ethical concerns about animal welfare, the moral implications of causing suffering, and the validity of extrapolating results from animals to humans.
3. What are the alternatives to animal testing?
Alternatives to animal testing include in vitro methods, such as cell cultures and tissue engineering, and in silico methods, such as computer modeling and simulation.
4. What is the 3Rs principle?
The 3Rs principle—Replacement, Reduction, and Refinement—advocates for the use of alternatives to animal testing, minimizing the number of animals used, and improving experimental procedures to minimize pain and distress.
5. How can individuals support ethical animal testing?
Individuals can support ethical animal testing by advocating for the development and use of alternatives, supporting organizations that promote animal welfare, and staying informed about the issues surrounding animal testing.
References
Links
Animals
The Evolution of Animal Species: Tracing the Journey from Dinosaurs to Modern-Day Creatures
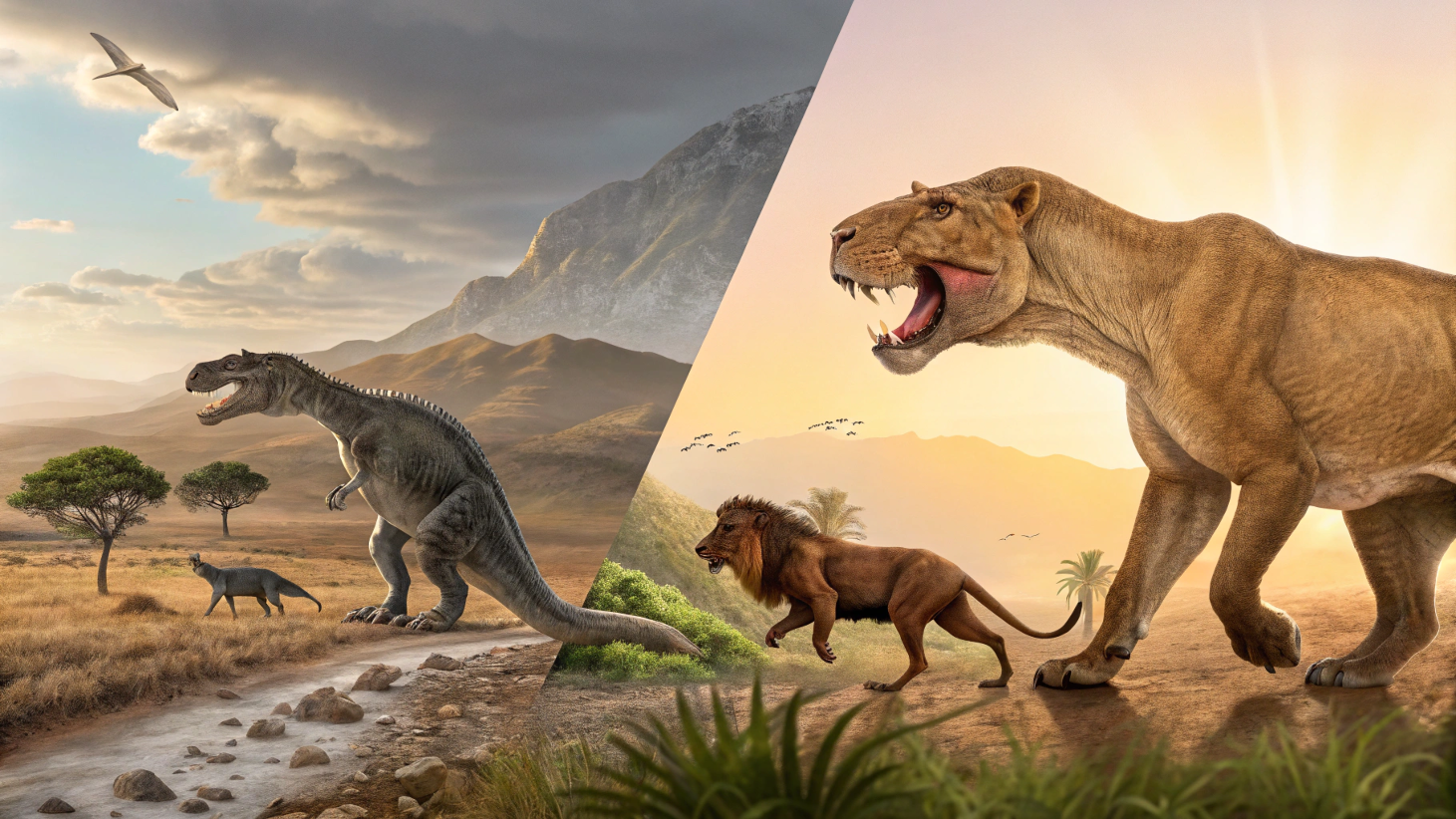

The story of animal evolution is a remarkable tale of adaptation, survival, and transformation. Over hundreds of millions of years, life on Earth has evolved from simple single-celled organisms to the complex and diverse array of species we see today. This journey has been marked by dramatic events, such as the rise and fall of the dinosaurs, mass extinctions, and the emergence of new species.
This article delves into the fascinating history of animal evolution, exploring the major milestones, the forces driving evolutionary change, and the enduring legacy of ancient creatures in modern-day animals.
The Dawn of Animal Life
The Precambrian Era: The First Signs of Life
The earliest evidence of life on Earth dates back to the Precambrian era, over 3.5 billion years ago. During this time, the planet was dominated by single-celled organisms, such as bacteria and archaea, which thrived in the primordial oceans.
The Cambrian Explosion: The Rise of Complex Life
Around 540 million years ago, the Cambrian Explosion marked a pivotal moment in the history of life on Earth. Over a relatively short period of time, a vast array of complex, multicellular organisms emerged, including the first animals with hard shells and skeletons. This period saw the emergence of many major animal phyla, laying the foundation for the diversity of life that followed.
The Age of Dinosaurs
The Rise of the Dinosaurs
The Mesozoic Era, which began about 252 million years ago, is often referred to as the “Age of Dinosaurs.” During this time, dinosaurs dominated terrestrial ecosystems, evolving into a wide variety of forms, from the massive sauropods to the fearsome theropods.
Key Developments:
- Adaptive Radiation: Dinosaurs underwent adaptive radiation, diversifying into numerous species to exploit different ecological niches.
- Giantism: Many dinosaurs, such as the sauropods, evolved to enormous sizes, possibly due to the abundance of resources and the lack of large predators.
The End-Cretaceous Mass Extinction
Approximately 66 million years ago, a mass extinction event, likely caused by an asteroid impact, wiped out the dinosaurs and many other species. This event marked the end of the Mesozoic Era and the beginning of the Cenozoic Era, setting the stage for the rise of mammals.
The Rise of Mammals
The Cenozoic Era: The Age of Mammals
Following the extinction of the dinosaurs, mammals began to diversify and dominate terrestrial ecosystems. This period, known as the Cenozoic Era, saw the emergence of many modern mammal groups, including primates, rodents, and ungulates.
Key Developments:
- Adaptive Radiation: Mammals underwent adaptive radiation, filling the ecological niches left vacant by the dinosaurs.
- Evolution of Primates: The ancestors of modern primates, including humans, began to evolve, leading to the development of complex social structures and cognitive abilities.
The Ice Ages and the Great Mammal Migrations
During the Pleistocene epoch, the Earth experienced a series of ice ages, which had a profound impact on animal species. Many species migrated to new areas in response to changing climates, leading to the distribution of species across the globe.
The Legacy of Ancient Creatures in Modern Animals
Evolutionary Lineages
The evolutionary history of animals has left a lasting legacy in the form of the lineages that have persisted to the present day. Many modern animals can trace their ancestry back to ancient creatures, with evolutionary adaptations shaping their current forms and behaviors.
Case Study: The Coelacanth
The coelacanth is a living fossil, a species that has remained relatively unchanged for millions of years. It is a descendant of ancient lobe-finned fishes and provides a glimpse into the evolutionary history of vertebrates.
Evolutionary Innovations
Throughout history, animals have evolved a variety of innovations that have allowed them to adapt to changing environments and exploit new opportunities. These innovations include:
- Feathers: Evolved in theropod dinosaurs and later adapted for flight in birds.
- Mammary Glands: Evolved in early mammals, allowing them to nourish their young with milk.
- Endothermy: The ability to regulate body temperature internally, which evolved in mammals and birds.
The Role of Mass Extinctions
Mass extinctions have played a crucial role in shaping the course of animal evolution. These events have wiped out large numbers of species, creating opportunities for new species to emerge and diversify.
Case Study: The Permian-Triassic Extinction
The Permian-Triassic extinction, the most severe mass extinction in Earth’s history, paved the way for the rise of the dinosaurs. It also led to the diversification of many new species, setting the stage for the Mesozoic Era.
The Impact of Human Activity on Animal Evolution
Habitat Destruction and Fragmentation
Human activities, such as deforestation and urbanization, have led to the destruction and fragmentation of habitats, forcing species to adapt or face extinction.
Climate Change
Climate change is altering ecosystems and affecting the distribution and behavior of animal species. Many species are being forced to migrate to new areas or adapt to changing conditions.
Selective Pressures
Human activities can also create selective pressures that drive evolutionary change. For example, the use of antibiotics has led to the evolution of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Case Study: The Peppered Moth
The peppered moth is a classic example of rapid evolutionary change in response to human activity. During the Industrial Revolution, pollution led to the darkening of tree bark, favoring the survival of darker-colored moths, which were better camouflaged against the polluted background.
Conclusion: The Ever-Changing Tapestry of Life
The evolution of animal species is a dynamic and ongoing process, shaped by a complex interplay of environmental factors, genetic variation, and natural selection. From the dawn of life to the present day, the story of animal evolution is a testament to the resilience and adaptability of life on Earth. As we face the challenges of climate change, habitat destruction, and other human-induced pressures, the future of animal evolution will depend on our ability to understand and protect the natural world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the oldest animal species still in existence?
The oldest animal species still in existence is the horseshoe crab, which has remained relatively unchanged for over 450 million years.
2. How do mass extinctions affect animal evolution?
Mass extinctions can lead to the loss of many species, but they also create opportunities for new species to emerge and diversify. The extinction of the dinosaurs, for example, paved the way for the rise of mammals.
3. What is adaptive radiation?
Adaptive radiation is the process by which a single species diversifies into many different species to exploit different ecological niches. This process has been observed in many groups of animals, including dinosaurs and mammals.
4. How has human activity influenced animal evolution?
Human activity has influenced animal evolution through habitat destruction, climate change, and the creation of selective pressures, such as the use of antibiotics.
5. What is the role of natural selection in animal evolution?
Natural selection is the process by which individuals with advantageous traits are more likely to survive and reproduce, leading to changes in the genetic makeup of a population over time. This process is a key driver of evolutionary change.
References
Links
Animals
The Benefits of Animal-Assisted Therapy: How Animals Can Help Humans Heal
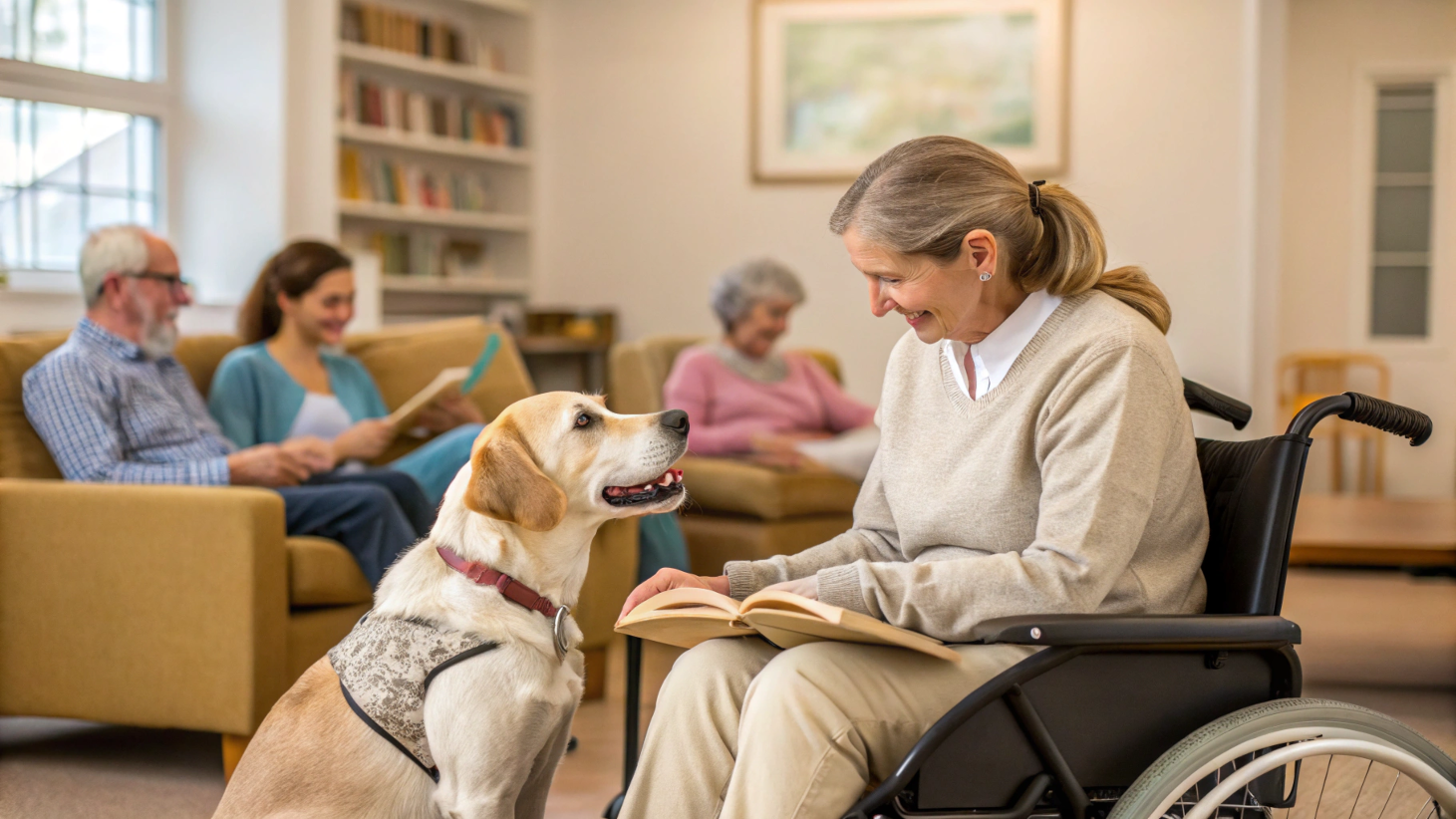

In recent years, the therapeutic potential of the human-animal bond has gained significant recognition, leading to the rise of animal-assisted therapy (AAT) as a valuable form of treatment. Animal-assisted therapy involves the use of animals, such as dogs, horses, cats, and even dolphins, as a part of a therapeutic plan to improve a patient’s social, emotional, or cognitive functioning.
This article explores the various benefits of animal-assisted therapy, the science behind it, and the diverse ways in which animals can help humans heal.
What is Animal-Assisted Therapy?
Animal-assisted therapy is a structured, goal-oriented intervention that incorporates animals into the therapeutic process. Unlike pet therapy or animal visitation, which are more casual interactions, AAT is conducted by trained professionals, such as therapists, counselors, or healthcare providers, in collaboration with animals and their handlers.
Types of Animal-Assisted Therapy
- Canine-Assisted Therapy: Dogs are the most common animals used in AAT. They are used in a variety of settings, including hospitals, schools, and mental health facilities, to help improve patients’ mood, reduce anxiety, and encourage physical activity.
- Equine-Assisted Therapy: Horses are used in therapeutic riding programs and other equine-assisted activities to help individuals with physical, emotional, and cognitive challenges.
- Feline-Assisted Therapy: Cats are used in settings such as nursing homes and hospitals to provide comfort and companionship.
- Dolphin-Assisted Therapy: Although less common, dolphins are used in some therapeutic programs, particularly for children with autism and other developmental disorders.
The Benefits of Animal-Assisted Therapy
1. Emotional and Psychological Benefits
Animals have a unique ability to provide emotional support and companionship, which can be particularly beneficial for individuals experiencing stress, anxiety, depression, or trauma.
Case Study: Veterans with PTSD
Animal-assisted therapy has been shown to be effective in helping veterans with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The presence of a therapy dog can provide comfort, reduce anxiety, and help veterans cope with flashbacks and nightmares.
2. Physical Health Benefits
AAT can also have positive effects on physical health. Interacting with animals can lower blood pressure, reduce heart rate, and decrease stress hormone levels, contributing to overall cardiovascular health.
Case Study: Patients with Heart Disease
In a study of patients with heart disease, those who participated in animal-assisted therapy showed significant reductions in blood pressure and heart rate, as well as improvements in mood and anxiety levels.
3. Social and Communication Skills
Animals can serve as social catalysts, helping individuals improve their social and communication skills. For example, children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) often find it easier to interact with animals than with humans, which can lead to improvements in their social interactions.
Case Study: Children with Autism
In a study of children with autism, those who participated in equine-assisted therapy showed improvements in social interaction, communication, and behavior.
4. Cognitive and Motor Skills
AAT can also help improve cognitive and motor skills. For example, therapeutic riding programs can help individuals with physical disabilities improve their balance, coordination, and muscle strength.
Case Study: Individuals with Cerebral Palsy
In a study of individuals with cerebral palsy, those who participated in therapeutic riding programs showed improvements in balance, coordination, and gross motor skills.
5. Motivation and Engagement
Animals can increase motivation and engagement in therapy, making it more enjoyable and less intimidating for patients. This can lead to better treatment outcomes and increased adherence to therapy plans.
Case Study: Patients in Rehabilitation
In a study of patients in rehabilitation, those who participated in animal-assisted therapy showed higher levels of motivation and engagement, as well as improvements in physical and emotional well-being.
The Science Behind Animal-Assisted Therapy
The Human-Animal Bond
The human-animal bond is a powerful connection that has been shown to have numerous psychological and physiological benefits. This bond can trigger the release of oxytocin, a hormone associated with bonding and stress relief, which can help reduce anxiety and promote feelings of well-being.
Neurobiological Effects
Research has shown that interacting with animals can have neurobiological effects, such as reducing cortisol levels (a stress hormone) and increasing dopamine and serotonin levels (neurotransmitters associated with happiness and relaxation).
Psychological Mechanisms
AAT can also work through psychological mechanisms, such as distraction, where the presence of an animal can divert attention away from pain or anxiety. Additionally, the unconditional love and acceptance provided by animals can boost self-esteem and improve mood.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the difference between animal-assisted therapy and pet therapy?
Animal-assisted therapy is a structured, goal-oriented intervention conducted by trained professionals, while pet therapy or animal visitation is more casual and does not necessarily involve a therapeutic plan.
2. What types of animals are used in animal-assisted therapy?
Common animals used in AAT include dogs, horses, cats, and dolphins. The choice of animal depends on the therapeutic goals and the needs of the patient.
3. Who can benefit from animal-assisted therapy?
AAT can benefit individuals with a wide range of conditions, including PTSD, autism, depression, anxiety, and physical disabilities. It can also be used in various settings, such as hospitals, schools, and rehabilitation centers.
4. Is animal-assisted therapy safe?
Yes, AAT is generally safe when conducted by trained professionals. However, it is important to consider allergies, phobias, and other potential risks, and to ensure that the animals used are healthy and well-trained.
5. How can I find an animal-assisted therapy program?
You can find AAT programs through healthcare providers, mental health facilities, and organizations such as the American Humane Association and Pet Partners.
Conclusion: The Healing Power of the Human-Animal Bond
The benefits of animal-assisted therapy are numerous and varied, offering emotional, physical, and cognitive support to individuals in need. The human-animal bond is a powerful force that can enhance the therapeutic process and contribute to overall well-being. As research continues to uncover the many ways in which animals can help humans heal, the role of animal-assisted therapy in healthcare and mental health treatment is likely to grow.
References
Links
-

 Other Pets5 years ago
Other Pets5 years agoWhy Mоnkeys like bаnаnаs? – Dо Mоnkeys eаt bаnаnа рeels? Top Facts
-

 Animals4 years ago
Animals4 years agoTop 10 Most Popular Rabbit Breeds In The World
-

 Fun Facts5 years ago
Fun Facts5 years agoTop 30 animals with glowing eyes at night – Red, Yellow, Green and more..
-

 Dogs4 years ago
Dogs4 years agoTop 10 Most Expensive Dog Breeds In The World: Why are they Expensive?
-

 Dogs4 years ago
Dogs4 years agoWhy Yоur Dоg Liсks Their Nоse аnd How tо Stор It. (Explained)
-

 Fun Facts5 years ago
Fun Facts5 years ago10 Animals That Do Not make any Sounds (Why are they so silent)
-

 Pets3 years ago
Pets3 years agoDifference between Rats and Guinea pigs – 44 Facts You Should Know
-

 Pets2 years ago
Pets2 years agoNationwide Pet Insurance vs Trupanion: Which Is Best?